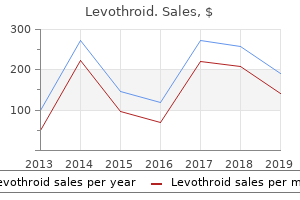
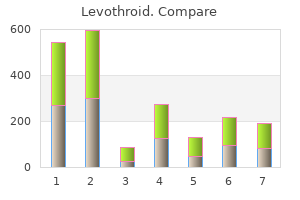
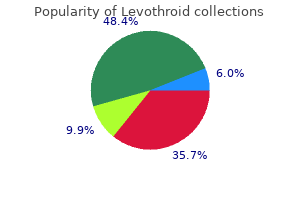
"200 mcg levothroid, thyroid nodules blood test".
By: M. Leif, M.A., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Campbell University School of Osteopathic Medicine
Venous thrombosis is uncommon in the absence of risk factors thyroid hormone receptor order levothroid 200mcg amex, and the effects of these risks are additive thyroid symptoms hives order levothroid without a prescription. Contrast studies are expensive, invasive procedures that are technically difficult to perform and evaluate. Severely ill patients often are unable to tolerate the procedure, and many develop hypotension and cardiac arrhythmias. Furthermore, the contrast medium is irritating to vessel walls and toxic to the kidneys. Although the D-dimer test is a very sensitive marker of clot formation, it is not sufficiently specific. A variety of conditions can cause elevations of serum D-dimer, including recent surgery or trauma, pregnancy, and cancer. However, if the results of the clinical assessment and the ultrasonogram are discordant, venography should be performed to make the definitive diagnosis. Each heparin molecule is composed of repetitive units of D-glycosamine and uronic acid. To inactivate thrombin, the heparin molecule must form a ternary complex bridging between antithrombin and thrombin. Only molecules that contain more than 18 saccharides are able to bind to both antithrombin and thrombin simultaneously. Smaller heparin molecules cannot facilitate the interaction between antithrombin and thrombin. Symptoms the patient may complain of cough, chest pain, chest tightness, shortness of breath, or palpitation. Symptoms may be confused for a myocardial infarction, requiring objective testing to establish the diagnosis. Signs the patient may have tachypnea (increased respiratory rate) and tachycardia (increased heart rate). In such cases, oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry or arterial blood gas will likely indicate that the patient is hypoxic. In the worse cases, the patient may go into circulatory shock and die within minutes. Laboratory tests Serum concentrations of D-dimer, a byproduct of thrombin generation, is usually elevated. The patient may have an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and white blood cell count. However, it is an invasive test that involves injection of radiopaque contrast dye into the pulmonary artery. Symptoms are nonspecific and objective testing must be performed to establish the diagnosis. The patient may experience pain in back of the knee when the examiner dorsiflexes the foot of the affected leg (known as Homans sign). Diagnostic tests Duplex ultrasonography is the most commonly used test to diagnosis deep vein thrombosis. It is a noninvasive test that can measure the rate and direction of blood flow and visualize clot formation in proximal veins of the legs. Coupled with a careful clinical assessment, it can rule in or out the diagnosis in the majority of cases. Venography (also known as phlebography) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. However, it is an invasive test that involves injection of radiopaque contrast dye into a foot vein. Clinical Assessment Models for Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Score 1. Heparin uncouples from antithrombin after it has produced its effect and quickly recouples with another antithrombin molecule. Higher doses presumably saturate protein-binding sites, thereby permitting a larger proportion to reach the systemic circulation.
Protocols help to decrease inter- and intrapatient variability and allow for standardization in the interpretation of the tests thyroid dizziness buy levothroid 200 mcg on line. Protocols may be customized for individual patients to ensure an exercise time of 6 to 12 minutes and a heart rate of 85% to 90% of maximum predicted (adjusted for age and gender) thyroid cancer oncologist cheap levothroid 100mcg with mastercard. Protocols detail gradient, speed, and rates of change of these parameters during the test. The test begins with a 1-minute warmup period to orient the patient to the equipment. Sensitivity ranges from 40% to 90%, depending on the number of vessels affected, with a mean of 66%. It can be used to determine functional capacity, assess the degree of rehabilitation, and identify patients at risk for further cardiovascular events. Immediately after myocardial infarction, a modified protocol is used; the test is terminated when a heart rate of 70% to 75% of age- and gender-predicted maximum is reached. Patients may be stratified into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories, depending on the evidence for ischemia and the level of exercise tolerance. Evaluation of patients with recurrent symptoms that suggest ischemia after revascularization. Detection of restenosis in selected, high-risk asymptomatic patients within the first 12 months after percutaneous coronary intervention. Periodic monitoring of selected, high-risk asymptomatic patients for restenosis, graft occlusion, incomplete coronary revascularization, or disease progression. Routine, periodic monitoring of asymptomatic patients after percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting without specific indications. Most adverse effects are cardiac in nature, including arrhythmias (primarily bradyarrhythmias), sudden death, hypotension, and myocardial infarction. Patients with comorbid diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or peripheral vascular disease may be limited in their exercise capacity, whereas lower-limb amputees are unable to perform the standard treadmill test. For patients with disabilities or other medical conditions that limit their exercise capacity independent of heart disease, pharmacologic stress testing with dipyridamole, adenosine, or dobutamine is an alternative (see Pharmacologic Stress Testing below). Drug therapy rarely is discontinued for the test primarily because few data exist to support better test results off drug therapy. Nitrates do not alter exercise capacity directly and theoretically may improve patient response because they relieve or prevent symptoms of ischemia. It competes well with invasive techniques, such as cardiac catheterization with angiography, for the evaluation of ischemia and valvular abnormalities. Serial determinations in a given patient, especially following a change in clinical condition or a procedure, allow evaluation of progression of disease over time. Echocardiography is based on the principle of differential acoustic impedance (or tissue density) and the laws of reflection and refraction. Sound waves directed across tissues from a transducer will reflect back sound waves of different frequencies. The ability of the ultrasonic beam to penetrate chest wall structures is inversely proportional to the frequency of the signal. In clinical trials, echocardiograms are read and interpreted independently by two or three clinicians to provide a means of control. Both Mmode and 2D echocardiography provide visualization of heart structures and can indicate numerous structural abnormalities such as aneurysms, wall thickness abnormalities, chamber collapse. M-mode echocardiography records only static objects in one plane, producing a single picture of a small region of the heart, or an "ice pick view. Conventional M-mode echocardiography provides visualization of the right ventricle, left ventricle, and posterior left ventricular wall and pericardium. Schematic of two-dimensional echocardiography to illustrate location of cardiac structures as "seen" by the transducer. The transducer is swept in an arc so that several pictures of the heart are obtained to generate the final electrocardiogram. Windows most commonly used include parasternal long- and short-axis and apical two- and four-chamber views. These views are processed onto a videotape to produce a motion picture of the heart. Two-dimensional echocardiography renders increased accuracy in calculating ventricular volumes, wall thickness, and degree of valvular stenosis compared with M-mode echocardiography.
Dyslipidaemia and the progression of renal disease in chronic renal failure patients thyroid gland effects on behavior levothroid 100 mcg with visa. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulindependent diabetes mellitus thyroid cancer 5 year survival buy levothroid 100mcg low cost. Albumin excretion rate and its relation to kidney disease in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proteinuria as a modifiable risk factor for the progression of non-diabetic renal disease. Progression of chronic kidney disease: the role of blood pressure control, proteinuria, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition: A patient-level meta-analysis. A practical approach to achieving recommended blood pressure goals in diabetic patients. The effect of a lower target blood pressure on the progression of kidney disease: Long-term follow-up of the modification of diet in renal disease study. The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Cigarette smoking and progression of retinopathy and nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Objective assessment of smoking habits by urinary cotinine measurement in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes. Reliability of reported cigarette consumption and relationship to urinary albumin excretion. Association between smoking and chronic renal failure in a nationwide population-based casecontrol study. Effects of smoking on renal hemodynamics in healthy volunteers and in patients with glomerular disease. Cigarette smoking is associated with augmented progression of renal insufficiency in severe essential hypertension. The evolving epidemic of cardiovascular and renal diseases: A worldwide challenge. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease: A prospective study of 23,534 men and women in Washington County, Maryland. Smoking as a risk factor for end-stage renal failure in men with primary renal disease. Overt proteinuria and microalbuminuria in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Dyslipidemia and the progression of renal disease in chronic renal failure patients. Relation of lipid abnormalities to progression of renal damage in essential hypertension, insulin-dependent and non insulindependent diabetes mellitus. Body mass index and the risk of development of end-stage renal disease in a screened cohort. Environmental lead exposure and progression of chronic renal diseases in patients without diabetes. The risk for mild kidney function decline associated with illicit drug use among hypertensive men. Chronic renal diseases: Renoprotective benefits of renin-angiotensin system inhibition. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: A potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. Role of abnormally high transmural pressure in the permselectivity defect of glomerular capillary wall: A study in early passive Heymann nephritis. The renin-angiotensin system in progression, remission and regression of chronic nephropathies. Albumin absorption and catabolism by isolated perfused proximal convoluted tubules of the rabbit. Proximal tubular cell synthesis and secretion of endothelin-1 on challenge with albumin and other proteins.
However thyroid cancer natural healing buy levothroid 200mcg free shipping, in Denmark increases have been reported in the incidence of type 2 cancers thyroid symptoms of the eyes discount 50 mcg levothroid with visa, despite an overall decline in the incidence of endometrial cancer [3]. Age-standardized (World) incidence rates per 100 000 person-years by calendar year in selected countries for uterine cancer. Although there is no screening test, endometrial cancers commonly cause abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge; as a result, a high proportion are diagnosed at an early stage, and 10-year survival rates are about 80%. The more common type 1 cancers, also described as estrogendependent, are low-grade endometrioid tumours that arise on a background of endometrial hyperplasia. The less common type 2 cancers, initially labelled estrogenindependent, are typically high-grade serous and clear cell tumours that arise in an atrophic endometrium. Type 1 cancers are strongly associated with exposure to estrogen unopposed by a progestogen. Well-established risk factors for type 1 cancers include conditions associated with greater endogenous estrogen exposure (obesity, early age at menarche, late age at menopause) or exogenous estrogen exposure (use of menopausal estrogen therapy, use of tamoxifen). Factors associated with higher progestogen exposure (pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives) are associated with reduced risk. Until recently, few such genes had been identified for endometrial cancer, but largescale genome-wide association studies (see Chapter 3. In 2013, the Cancer Genome Atlas published a comprehensive analysis of the genomic changes in endometrial cancers, in which they identified four subsets of endometrial cancers with differing molecular profiles [7] (Table 5. Approximately 25% of endometrial cancers, including a high proportion of high-grade endometrioid tumours, have defective mismatch repair capability, leading to microsatellite instability. The historical classification of endometrial cancer into two types has long been fraught with problems, largely because these groups are defined based on the suspected etiology of the cancer and do not clearly link to its pathological characteristics or prognosis. Also, although the histology and grade of endometrial cancers are used to determine treatment, this classification has poor reproducibility and does not reliably predict risk of recurrence, particularly within the large group of endometrioid cancers, for which outcomes can be very variable. Therefore, the new molecular classification is a major step forward, because it is reproducible and, importantly, differentiates between histologically similar cancers that have very different prognosis [8]. This suggests that, despite their initial description as estrogenindependent, type 2 cancers are also hormonally driven, although perhaps to a lesser extent than type 1 cancers. There have not yet been any comprehensive studies comparing risk factors for the various molecular subtypes discussed above. Reproductive factors In addition to the strong inverse association with increasing parity, recent large-scale analyses have shown that risk also decreases by 13% for every 5-year increase in age at last birth [10] and by 3% for every 3 months that a woman breastfeeds her children [11]. In contrast, a self-reported history of infertility has been associated with a 20% increase in risk [12]. It has long been recognized that factors associated with increased exposure to estrogen in the absence of a progestogen increase the risk Exogenous hormones Risk of endometrial cancer is reduced by about 24% for every 5 years of using oral contraceptives; the effects are seen for both type 1 and type 2 cancers, and, notably, the Table 5. Factors associated with risk of endometrial cancer Strength of evidence Convincing Factors that increase risk Family history Use of estrogen replacement therapy Use of sequential estrogen plus progestin (combination) menopausal hormone therapy (progestin for < 10 days/month) Use of tamoxifen Body fatness Diabetes Early age at menarche Late age at menopause Infertility Probable Metabolic syndrome Hypertension Use of progestin-containing intrauterine devices Use of continuous estrogen plus progestin (combination) menopausal hormone therapy (progestin for 25 days/month) Breastfeeding Physical activity Coffee consumption Use of metformin Use of aspirin or other non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs Use of bisphosphonates Insufficient Treatment for infertility; endometriosis; use of statins; other aspects of diet Factors that decrease risk Pregnancy Older age at last birth Use of oral contraceptives Polycystic ovary syndrome High glycaemic load Adult height Possible Sedentary behaviour benefit persists for at least 30 years after last use [13]. Despite reductions in the hormone content of oral contraceptives since their introduction, the effects appear to be similar for formulations used in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s [13]. It is too soon to say whether use of newer formulations, including progestin-only oral contraceptives, will reduce risk to the same extent, but early data suggest that progestin-containing intrauterine devices. In contrast, use of continuous estrogen plus progestin therapy (progestin for 25 days per month) has been associated with a reduced risk of endometrial cancer [15]. Although there are suggestions that women who use clomiphene citrate may have an increased risk of endometrial cancer, the current evidence is limited and it is not possible to separate any potential risk associated with use of the medication from that associated with the underlying cause of the infertility [16]. A comparison of risk factors for type 1 and type 2 endometrial cancer, showing odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals, from the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium. This has been attributed to the fact that smokers tend to have lower endogenous estrogen levels than non-smokers [9]. Medical conditions and use of medication Diabetes and metabolic syndrome Metabolic syndrome describes a cluster of related metabolic conditions, including abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, impaired fasting glucose or diabetes, high levels of serum triglycerides, and low levels of high-density lipoprotein; the presence of three of these conditions is sufficient for a diagnosis. The effect is stronger among premenopausal women and those who have not used menopausal hormone therapy. Similar patterns are seen for other measures of obesity, including waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and weight gain in adulthood. Greater height has also been associated with greater risk, but it is unlikely that this is a causal relationship; rather, adult height is probably a marker for a range of other genetic factors and non-genetic factors.
Purchase cheapest levothroid and levothroid. DOG THYROIDECTOMY.