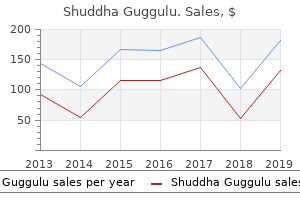
"Buy genuine shuddha guggulu on line, weight loss shots".
By: T. Kelvin, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine
Lack of clinical relevance of routine chest radiography in acute psychiatric admissions weight loss percentage calculator proven shuddha guggulu 60caps. Use and accuracy of diagnostic imaging by hospital type in pediatric appendicitis weight loss pills 901 cheap 60caps shuddha guggulu amex. Interrater reliability of clinical findings in children with possible appendicitis. About the American College of Surgeons the American College of Surgeons is a scientific and educational organization of surgeons that was founded in 1913 to raise the standards of surgical practice and to improve the quality of care for surgical patients. Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients. The College has more than 79,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. Anti-caries (anti-cavities) benefit begins with eruption of the first primary tooth. Use of recommended amounts of fluoride toothpaste minimize risks of fluorosis, a whitish discoloration of enamel. High quality evidence shows sealants are safe and effective in arresting caries progression in initial stage (incipient) non-cavitated, occlusal caries. Sealants offer a tooth-preserving treatment when compared to restorations, which may require removal of some healthy tooth structure, thereby weakening the tooth and increasing the risk that the tooth will eventually require more extensive treatment. Applying sealants as soon as initial stage caries is detected can improve outcomes by minimizing the later need for more extensive restorative care. Some children do not respond to communicative behavior guidance techniques and require treatment of dental disease. Advanced behavior guidance techniques of sedation, protective stabilization, and general anesthesia offer risks and benefits often beyond the health knowledge of parents and other caretakers. Informed consent best practice requires a thorough, understandable explanation of these techniques and alternatives including deferral of treatment with its inherent risks. Therefore, management is generally conservative and includes reversible strategies such as patient education, medications, physical therapy and/or the use of occlusal appliances that do not alter the shape or position of the teeth or the alignment of the jaws. Dental restorations (fillings) fail due to excessive wear, fracture of material or tooth, loss of retention, or recurrent decay. The larger the size of the restoration and/or the greater the number of surfaces filled increases the likelihood of failure. Restorative materials have different survival rates and fail for different reasons, but age should not be used as a failure criteria. Patients with any specific questions about the items on this list or their individual situation should consult their dentist. The Steering Committee reviewed critical issues in dentistry to identify potential recommendation topics and developed, through an evidence-based process, a list of recommendation statements with supporting scientific evidence. Via an intense consensus process, the Steering Committee prepared a list of recommendation statements which were sent to the Council on Access, Prevention and Interprofessional Relations for review. Fluoride toothpaste efficacy and safety in children younger than 6 years: a systematic review. Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in the permanent teeth of children and adolescents. Evidence-based clinical recommendations for the use of pit-and-fissure sealants: a report of the American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. Update on nonsurgical, ultraconservative approaches to treat effectively non-cavitated caries lesions in permanent teeth. Sealing versus partial caries removal in primary molars: a randomized clinical trial. Systematic review of noninvasive treatments to arrest dentin non-cavitated caries lesions. Pit and fissure sealants: evidence-based guidance on the use of sealants for the prevention and management of pit and fissure caries. Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: an update. Guideline for Monitoring and Management of Pediatric Patients During and After Sedation for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Pediatr Dent.
In agreement with these observations weight loss 1200 calorie diet order shuddha guggulu 60 caps amex, veterinary reports of animals that ingest aflatoxin found in moldy hay have documented suppressed cell-mediated immune responses with reduced phagocytosis and depressed production of complements and interferon weight loss lemon water buy shuddha guggulu 60caps with visa. Acquired immunity from vaccination programs has also been shown to be substantially suppressed (Pier 1992). Two episodes of severe aflatoxin poisoning were reported in horses, with encephalomalacia of cerebral hemispheres, fatty degeneration, necrosis, bile duct hyperplasia, fibrosis of the liver, fatty infiltration of the kidney, hemorrhagic enteritis, and myocardial degeneration. The diagnosis was based on gross and histopathologic observations, consistent with observations of other species poisoned with aflatoxin, and on isolation of the toxin from feed and animal tissues (Angsubhakorn et al. It is associated with ingestion of foodstuffs made from barley that was not dried after harvest and was stored through the fall and winter in moist conditions, typically in Yak-skin and Yak-hair bags (Allander 1994, Haubruge et al. This food-related disease has occurred sporadically in Russia, probably since the nineteenth century. Various reports indicate that chronic consumption of grain contaminated with a trichothecene (T-2) mycotoxin resulted in a mortality rate of 10-60 percent of the local population during the years 1942-1947 (Locasto et al. The first phase develops within 72 hours of initial consumption of the contaminated foodstuffs. It results in gastrointestinal inflammation leading to abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, often accompanied by headache, weakness, fatigue, and tachycardia. The second, or "latent," phase is characterized by development of leukopenia and progressive lymphocytosis, and the third phase is heralded by the appearance of cherry-red petechial rashes, which gradually expand and become confluent on the trunk and extremities. This can be accompanied by bleeding diatheses in the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal mucosa. If patients survive these insults, they may expire from secondary infections, including pneumonia. If they do recover, the convalescence can be protracted, with up to 8 weeks required for recovery of bone marrow leukopoiesis and peripheral cell counts (Wannemacher and Wiener 1997). There is also evidence of potent effects produced in farm animals that have consumed feed contaminated by trichothecene mycotoxins; the effects in poultry include excess mortality, reduced growth rates, beak deformities, and compromised immune systems. In mammals (cattle and swine), slow growth, lowered milk production, sterility, hemorrhagic bowel syndrome, and death can occur (Jacobsen et al. Thus a variety of clinical reports, as well as supporting laboratory studies, lend credence to the idea that ingestion of sufficient quantities of mycotoxins can cause significant disease or even death in humans and lower animals. Toxicity from Effects of Parenteral Exposure to Mycotoxins It is thought that the events in Orenberg in the 1940s led to the recognition of the potential use for T-2 and other trichothecene mycotoxins in biological warfare. It is further thought that subsequent weaponizing of T-2 toxins occurred, and that these agents were used in "yellow rain" attacks in Cambodia, Afghanistan, and Iraq, (Wannemacher and Wiener 1997, Bennion and David-Bajar 1994, Kianifar et al. These weaponized toxins are lipophilic and easily cross human skin, gut, and pulmonary epithelium. Following direct contact, they cause severe eye and skin irritation (erythema, edema, and necrosis) in humans, and at larger doses can yield incapacitation and death within minutes to hours. After respiratory exposure to these toxins, human victims can develop nasal pain and epistaxis, sore throat, vocal changes, cough, dyspnea, and hemoptysis (Wannemacher and Wiener 1997, Kortepeter et al. In toxicology studies in laboratory animals, mice, rats, and guinea pigs die within 12 hours of inhaling high doses of these aerosolized trichothecene mycotoxins, with no evidence of pulmonary edema or lung lesions. Effects of Inhaled Mycotoxins There is additional evidence of the deleterious effects of inhaled mold spores or mycotoxins (beyond the exposure to massive quantities of mycotoxins in biological warfare noted above). It is characterized by a flu-like syndrome with prominent respiratory symptoms and fever, which occurs abruptly a few hours after a single, heavy exposure to dust containing organic material including fungi. A case report suggested that neurotoxicity can also occur after airborne exposure to mycotoxins; Gordon reported a 16-year-old farmhand with encephalopathy consisting of progressive somnolence, slowness of thinking, and incapacitating tremors after being exposed to these agents while removing moldy fodder from a silo (Gordon et al. The literature that raises concerns regarding neurotoxicity is summarized by Baldo et al. An excellent review and carefully presented study, it demonstrates the problems clinicians face when evaluating complaints of memory loss, difficulty concentrating, or personality change in patients attributing their symptoms to mold exposure. The problems include poorly defined exposures to mold, less-well-defined exposure to mycotoxins, lack of a consistent pattern of deficits on neuropsychological testing that would begin to define a syndrome of toxicity attributable to mold, and the presence of other morbidities, such as depression, that can result in measurable impairment on neuropsychological tests. While clinical and epidemiologic data remain elusive, case reports are worrisome, and the subject remains open to further investigation.
If an advanced airway is placed weight loss pills that work over the counter generic 60caps shuddha guggulu free shipping, ventilations should not exceed 10 breaths/minute (1 breath every 6 seconds or 1 breath every 10 compressions) in adults weight loss 60 days buy shuddha guggulu 60 caps with amex. Pediatric Consideration: For children with an advanced airway, 1 breath every 3-5 seconds is recommended (equivalent to 12-20 breaths/minute) 3. Consider additional monitoring with biometric feedback which may improve compliance with suggested Resuscitation section guidelines 4. Chest compressions are usually the most rapidly applied therapy for the patient in cardiac arrest and should be applied as soon as the patient is noted to be pulseless. If the patient is being monitored with pads in place at the time of arrest, immediate defibrillation should take precedence over all other therapies, however, if there is any delay in defibrillation (for instance, in order to place pads), chest compressions should be initiated while the defibrillator is being applied. There is no guidance on how long these initial compressions should be applied; however, it is reasonable to either complete between 30 seconds and 2 minutes of chest compressions in cases of no bystander chest compressions or to perform Updated November 23, 2020 108 5. Patients should therefore be resuscitated as close to the point at which they are first encountered and should only be moved if the conditions on scene are unsafe or do not operationally allow for resuscitation b. There is uncertainty regarding the proper goals for oxygenation during resuscitation i. This should not be continued into the post-resuscitation phase in which the goal should be an oxygen saturation of 94-98%. Pediatric Considerations: Special attention should be applied to the pediatric population and airway management/respiratory support. However, the order of Circulation-Airway-Breathing is still recommended as the order of priority by the American Heart Association for pediatric resuscitation in order to ensure timely initiation of chest compressions to maintain perfusion, regardless of the underlying cause of the arrest 109 Updated November 23, 2020 ii. Position the patient in the supine position with a second rescuer performing manual uterine displacement to the left in an effort to displace the gravid uterus and increase venous return by avoiding aorto-caval compression iii. This position is less desirable than the manual uterine displacement as chest compressions are more difficult to perform in this position iv. Chest compressions should be performed slightly higher on the sternum than in the non-pregnant patient to account for elevation of the diaphragm and abdominal contents in the obviously gravid patient v. High-performance systems should practice teamwork using "pit crew" techniques with predefined roles and crew resource management principles. During the first four cycles of compressions/defibrillation (approximately 10 minutes) avoid advanced airway placement vi. One responding provider assumes code leader position overseeing the entire response vii. Part 11: Pediatric Basic Life Support: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Minimally interrupted cardiac resuscitation by emergency medical services for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Part 6: alternative techniques and ancillary devices for cardiopulmonary resuscitation: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Part 12: Pediatric Advanced Life Support: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Amiodarone as compared with lidocaine for shock-resistant ventricular fibrillation. The cardiocerebral resuscitation protocol for treatment of out-of-hospital primary cardiac arrest. Improved patient survival using a modified resuscitation protocol for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Implementation of pit crew approach and cardiopulmonary resuscitation metrics for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest improves patient survival and neurological outcome. Acute hospital administration of amiodarone and/or lidocaine in shockable patients presenting with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a nationwide cohort study. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: update and simplification of the Utstein templates for resuscitation registries. Part 5: Adult Basic Life Support: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Part 4: systems of care and continuous quality improvement: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Amiodarone for resuscitation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest due to ventricular fibrillation.

Intracerebral hemorrhages are most often found in the basal ganglia weight loss diet plans buy genuine shuddha guggulu on-line, cerebellum weight loss pills similar to adipex cheap shuddha guggulu 60 caps on line, brain stem, or cortex. The most common cause of an intracerebral hemorrhage is hypertension, especially if it is uncontrolled. Less common causes include trauma, infections, tumors, blood clotting deficiencies, and abnormalities in blood vessels (arteriovenous malformations). Figure 42 Intracerebral hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhages occur when a blood vessel just outside the brain ruptures, causing bleeding in the area between the brain and the meningeal layers, particularly the subarachnoid space. The sudden buildup of pressure outside the brain may also cause rapid loss of consciousness or death. Subarachnoid hemorrhages due to injury are often seen in the elderly who have fallen and hit their head. In younger people, motor vehicle crashes are the most common injury leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Important risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage include heavy alcohol use, cigarette smoking, hypertension, and possibly oral contraceptive use. A positive family or past personal history of subarachnoid hemorrhage also increases risk. Cerebral aneurysms are abnormalities of the arteries, often found at the base of the brain. Eighty to eight five percent of these lesions are in the anterior cerebral circulation (internal carotid artery and its branches), with the remainder located in the posterior circulation (vertebral arteries and its branches). Multiple cerebral aneurysms are found in approximately twenty five percent of cases. Small areas of rounded or irregular swellings in the arteries can cause the vessel walls to become weak and prone to rupture, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke. Ruptured intracranial aneurysms account for approximately eighty percent of non-trauma subarachnoid hemorrhages. Death can occur if the intracranial pressure is high enough to cause irreversible structural damage or halt cerebral perfusion. The prevalence of aneurysms is two hundred times higher than the annual incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage, leading to the conclusion that most aneurysms do not rupture. Treatment of the ruptured aneurysm is recommended as soon as tolerable by the patient, with the goal of obliterating the aneurysm within one to three days after the hemorrhage. Microsurgical aneurysm clipping and endovascular coil embolization are two very popular treatments. In microsurgical clipping, the neurosurgeon opens the dura, identifies the parent vessel and the ruptured aneurysm, and clips the aneurysm to exclude it from circulation. Endovascular coiling uses a micro-catheter threaded through a guide catheter to the origin of the ruptured aneurysm. Once inside the aneurysm, platinum coils are inserted into the sac until the aneurysm is densely packed. Coil therapy requires serial monitoring of patients and follow-up cerebrovascular imaging to detect the occasional risk of coil compaction or aneurysm recanalization. Initial treatment yields approximately seventy percent of patients experiencing ninety five to one hundred percent occlusion of the aneurysm. However, twenty five to thirty percent of patients do not have complete obliteration of their aneurysms, and recanalization can occur. The decision to proceed with open surgical clipping or endovascular treatment of an intracranial aneurysm after subarachnoid hemorrhage depends on both aneurysm-specific factors (location, size, morphology, and presence of thrombus), and patient-specific factors (age, density of the subarachnoid hemorrhage, patient preference, and other medical comorbidities). Concussions occur when the head or body is hit hard, or violently jarred or shaken. This causes the brain to crash into the skull, resulting in a disturbance of brain function. Problems can persist for months or even years in as many as thirty percent of patients. More than ten years ago, a federal study labeled concussions as "a serious public health problem", costing the United States an estimated eighty billion dollars per year. Regardless of how a concussion occurs- whether it is due to an accident, athletic event, or combat- it can lead to permanent loss of higher level mental processes. As the media continues to keep the issue of concussions in the forefront of the news, researchers are working with imaging modalities to better detect the subtle brain damage that concussions can cause.
Order shuddha guggulu online from canada. Dr. Dirk Rodriguez - Preparing for Weight Loss Surgery.