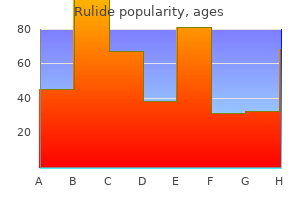
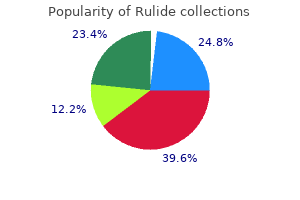
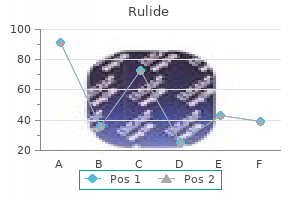
"Order rulide online pills, medications emts can administer".
By: A. Marik, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Virginia School of Medicine
Barium radiography is noninvasive medications borderline personality disorder discount rulide master card, costs less than endoscopy medicine 877 order rulide us, and is readily available but has significant disadvantages, particularly in patients who are bleeding briskly. Large amounts of retained blood or food in the upper gastrointestinal tract impede the mucosal coating by barium and therefore the localization of superficial mucosal lesions. In patients who are bleeding briskly and are hemodynamically unstable, contrast radiography is also impractical. Moreover, on occasion, multiple lesions may be detected by barium radiography and the actual site of bleeding may be difficult to assess. Barium contrast radiography is an acceptable alternative for diagnosing upper gastrointestinal lesions in patients who have not bled excessively, who have no stigmata of chronic liver disease, and who are not in need of endoscopic hemostasis. In those infrequent instances when the site of upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding is missed on endoscopy, angiography may localize the bleeding. In addition, selective infusion with vasopressin or coil embolization of actively bleeding arteries may control bleeding. In most instances, angiography localizes the bleeding site but does not establish its cause. Bleeding must also be active (>30 mL/h) because angiography detects only extravasation of contrast medium into the gastrointestinal tract. Angiography is expensive, time-consuming, and invasive and requires transporting the patient to a specialized unit, but it is particularly helpful if bleeding is brisk in the face of a negative evaluation of the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. For patients with less active blood loss, technetium red cell nuclear scintigraphy ("red cell scan") can localize the site of bleeding, with adequate sensitivity maintained 657 with as little as 3 mL of blood loss per hour. As with angiography, the sensitivity of technetium scintigraphy is limited, because active hemorrhage is needed; therefore, frequent repeat scanning is necessary. Technetium red cell scanning is often performed before any angiographic evaluation to prove the presence of active bleeding and to assist in the localization of the bleeding focus. Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding Colonic diverticula are responsible for nearly one fourth of all episodes of hemodynamically significant bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (see Table 123-2). Diverticular hemorrhage is nearly always painless and associated with acute large-volume hematochezia. Patients with clinical diverticulitis rarely bleed significantly (see Chapter 136). Colonic cancers and polyps often present as hematochezia, particularly with lesions in the distal sigmoid colon and rectum. Proximal colonic polyps and cancers, however, cause iron deficiency anemia and frequently dark black or bloody stools. Significant lower gastrointestinal tract bleeding also occurs from abnormal, superficial vessels called vascular ectasias (Color Plate 2 F); up to 10% of cases of hemodynamically significant hematochezia are caused by bleeding from upper gastrointestinal sites, particularly from duodenal bulbar ulcers (see Table 123-2). Proctoscopy, whether by rigid or flexible instruments, and careful evaluation of the anorectal junction are the initial diagnostic step for all patients with hematochezia. The anus and anorectal junction must be carefully examined for hemorrhoids or lacerations, because documented brisk bleeding from one of these sources can obviate the need for further invasive or non-invasive imaging. Blood from a very distal site in the rectum may reflux proximally into the colon and appear to come from above the maximal depth of insertion of the proctoscope or sigmoidoscope. Diverticula, rectal lacerations, colitis, and many polyps and cancers are found within reach of a flexible sigmoidoscope. If blood loss is modest (as evidenced by a normal hematocrit and vital signs), sigmoidoscopy may be followed by double-contrast barium radiography, which is highly accurate for detecting even smaller polyps and superficial mucosal abnormalities such as colitis. If signs and symptoms indicate lower gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage together with anemia, colonoscopy should be performed. The colon can be rapidly cleansed within a few hours, using oral polyethylene glycol-based electrolyte solutions. Colonoscopic evaluation not only allows the site of hemorrhage to be determined accurately but also allows biopsy of suspicious mass lesions, polypectomy for modest-sized polyps, and the use of coagulation techniques to control bleeding from vascular ectasias. Upper endoscopic evaluation should be performed in all patients with hematochezia who also have "coffee grounds" nasogastric lavage, in patients with known or suspected ulcer disease, and when brisk bleeding continues to cause profuse hematochezia. Technetium red blood cell scintigraphy can detect active bleeding at a rate of at least 3 to 10 mL/hr. Technetium red cell scintigraphy usually localizes the site but not the cause of active hemorrhage. If bleeding continues at a rate exceeding 30 to 50 mL/hr, angiography can be extremely helpful in localizing the site of hemorrhage. In addition, angiographic therapy is possible with vasopressin or embolization techniques.
Although physician-patient counseling may not always result in behavior change medications education plans order rulide 150mg fast delivery, it can be a powerful educational message delivered by a trusted authority medicine omeprazole order rulide american express. Medical and nursing professional organizations have prepared guidelines for institutionalizing the health care response to family violence through the development of model protocols, staff training materials, and proposed modification of intake forms for hospitals and clinics. Policies and procedures should be adapted to individual hospital needs and address state-specific regulations about reporting abuse to authorities. Health care providers can best assist abused patients by working collaboratively with local social and legal services and by referring patients to these resources. Tertiary prevention involves minimizing functional disability, a consequence of serious injury. Physicians can help their patients return to productive lives by ensuring that patients receive appropriate physical and occupational therapy and that they have access to community services after discharge. The independent living movement and local centers for independent living, as well as state departments of rehabilitation, can provide role models and resources for people with disabilities. Because community social and mental health services are essential for prevention and rehabilitation, physicians can serve their patients by publicly speaking out in support of these services. Information about the mechanisms and intentionality of injury must be gathered by coroners, medical examiners, and health care providers through history taking and documentation in official records. The usefulness of non-fatal injury data would be increased if all states established centralized hospital and emergency department databases that included external cause of injury codes. Physicians have played a leadership role in injury control in such diverse areas as traffic safety, burns from tap water and clothing ignition, and firearms policy. Legislators and journalists turn to physicians for information about disease and injury because physicians have daily contact with sick and injured people and can thus speak from personal experience about the problem. Informed physicians can advocate for solutions by testifying at legislative hearings, by granting media interviews, by making presentations at professional meetings, and by teaching medical students and residents about injury prevention principles and strategies. The World Wide Web sites suggested in the reference section provide the most recent data on statistics, policies, and programs related to violence and injury. The following agencies can direct investigators to additional sources of data, background materials, rationale for specific policies, and updates on the current status of policy initiatives and program interventions. Federal government information about criminal justice from the Justice Information Center at Federal government information from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration at Orenstein Immunization is one of the most cost-effective means of preventing morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases. Routine immunization, particularly of children, has resulted in decreases of 90% or more in reported cases of measles, mumps, rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, polio, tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. In many circumstances, immunization not only prevents morbidity and mortality but also, in the long run, reduces health care costs. Administering a vaccine or toxoid causes the body to produce an immune response against the infectious agent or its toxins. Vaccines consist of suspensions of live (usually attenuated) or inactivated microorganisms or fractions thereof. Toxoids are modified bacterial toxins that retain immunogenic properties but lack toxicity. Active immunization generally results in long-term immunity, although the onset of protection may be delayed because it takes time for the body to respond. With live attenuated vaccines, small quantities of living organisms multiply within the recipient until an immune response cuts off replication. In contrast, inactivated vaccines and toxoids contain large quantities of antigen. In the majority of recipients, a single dose of a live vaccine generally induces an immune response that closely parallels natural infection and induces long-term immunity. Passive immunization using immune globulins or antitoxins delivers pre-formed antibodies to provide temporary immunity. Immune globulins obtained from human blood may contain antibodies to a variety of agents, depending on the pool of human plasma from which they are prepared. Specific immune globulins are made from the plasma of donors with high levels of antibodies to specific antigens, such as tetanus immune globulin. Antitoxins are solutions of antibodies derived from animals immunized 41 with specific antigens.
Therefore symptoms 9dpo bfp order rulide uk, the ancestor of chromalveolates is believed to have resulted from a secondary endosymbiotic event treatment with chemicals or drugs buy generic rulide 150mg. However, some chromalveolates appear to have lost red alga-derived plastid organelles or lack plastid genes altogether. Therefore, this supergroup should be considered a hypothesis-based working group that is subject to change. Chromalveolates include very important photosynthetic organisms, such as diatoms, brown algae, and significant disease agents in animals and plants. Alveolates: Dinoflagellates, Apicomplexians, and Ciliates A large body of data supports that the alveolates are derived from a shared common ancestor. The alveolates are named for the presence of an alveolus, or membrane-enclosed sac, beneath the cell membrane. The exact function of the alveolus is unknown, but it may be involved in osmoregulation. The alveolates are further categorized into some of the better-known protists: the dinoflagellates, the apicomplexans, and the ciliates. Dinoflagellates exhibit extensive morphological diversity and can be photosynthetic, heterotrophic, or mixotrophic. Two perpendicular flagella fit into the grooves between the cellulose plates, with one flagellum extending longitudinally and a second encircling the dinoflagellate (Figure 23. Together, the flagella contribute to the characteristic spinning motion of dinoflagellates. These protists exist in freshwater this OpenStax book is available for free at cnx. Many are encased in cellulose armor and have two flagella that fit in grooves between the plates. Some dinoflagellates generate light, called bioluminescence, when they are jarred or stressed. Large numbers of marine dinoflagellates (billions or trillions of cells per wave) can emit light and cause an entire breaking wave to twinkle or take on a brilliant blue color (Figure 23. For approximately 20 species of marine dinoflagellates, population explosions (also called blooms) during the summer months can tint the ocean with a muddy red color. This phenomenon is called a red tide, and it results from the abundant red pigments present in dinoflagellate plastids. In large quantities, these dinoflagellate species secrete an asphyxiating toxin that can kill fish, birds, and marine mammals. Red tides can be massively detrimental to commercial fisheries, and humans who consume these protists may become poisoned. Apicomplexan life cycles are complex, involving multiple hosts and stages of sexual and asexual reproduction. By beating their cilia synchronously or in waves, ciliates can coordinate directed movements and ingest food particles. Certain ciliates have fused cilia-based structures that function like paddles, funnels, or fins. Ciliates also are surrounded by a pellicle, providing protection without compromising agility. The genus Paramecium includes protists that have organized their cilia into a plate-like primitive mouth, called an oral groove, which is used to capture and digest bacteria (Figure 23. Food captured in the oral groove enters a food vacuole, where it combines with digestive enzymes. Waste particles are expelled by an exocytic vesicle that fuses at a specific region on the cell membrane, called the anal pore. In addition to a vacuole-based digestive system, Paramecium also uses contractile vacuoles, which are osmoregulatory vesicles that fill with water as it enters the cell by osmosis and then contract to squeeze water from the cell. The micronucleus is essential for sexual reproduction, whereas the macronucleus directs asexual binary fission and all other biological functions. The process of sexual reproduction in Paramecium underscores the importance of the micronucleus to these protists. This process begins when two different mating types of Paramecium make physical contact and join with a cytoplasmic bridge (Figure 23. The diploid micronucleus in each cell then undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid micronuclei.
Simple spirometry and an arterial blood gas measurement are the only tests routinely required symptoms 39 weeks pregnant rulide 150mg sale. When pulmonary function does not appear to be evenly distributed between right and left lungs medical treatment purchase generic rulide line, perfusion scanning, which correlates well with regional pulmonary function, may help estimate postoperative pulmonary function. The roles of exercise testing and pulmonary artery pressure measurement are unclear. With the advent of lung-sparing operations, including sleeve-and-wedge resections, many patients who previously would not have been considered surgical candidates are now undergoing pulmonary resection. Close collaboration between internists and thoracic surgeons is necessary to determine whether marginal candidates are indeed appropriate for surgical therapy. Since the late 1960s, operative mortality has dropped from 10 to 20% to approximately 3%. The incidence of "fruitless thoracotomy," in which a lesion is discovered to be inoperable at the time of thoracotomy, has decreased from 25% to approximately 5%. The increased use of lung-sparing resections including sleeve lobectomy, segmentectomy, wedge resection, and thoracoscopic wedge resection has allowed surgical therapy to be applied to a group of patients with less pulmonary reserve than in the past. Although a prospective trial comparing conventional lobectomy with wedge resection has demonstrated that local recurrence rates are higher with the latter procedure, wedge resection is still an acceptable alternative in patients with diminished pulmonary reserve. Before a decision for surgical therapy is made in a given patient, three questions must be addressed (Fig. With the exception of peripheral solitary pulmonary nodules without hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy, a firm tissue diagnosis should almost always be obtained prior to surgical therapy. General medical criteria, such as absence of a recent myocardial infarction, should be applied. In addition, physiologic assessment should determine whether the planned resection will leave the patient with adequate pulmonary reserve. This answer requires adequate staging with detection of both distant metastases and local lymph node involvement. Significant physiologic impairment does result, however, so most patients who might be considered for curative radiation therapy are also candidates for curative surgical therapy. Although few trials of radiation therapy have been undertaken in early-stage lung cancer, an estimated 10 to 20% of localized lesions can be cured by radiation. Radiation therapy is often 454 Figure 85-1 Questions to determine therapy for lung cancer. A number of drugs are frequently used: cisplatin, carboplatin, paclitaxel, mitomycin, vinca alkaloids, ifosfamide, and etoposide. Newer regimens, such as carboplatin and paclitaxel, have improved activity over the regimens with which most controlled trials have been performed. Survival is reduced and side effects of chemotherapy are increased in patients who are not fully ambulatory; benefits to this group are likely to be minimal. Many experts believe that regimens containing etoposide and either carboplatin or cisplatin offer the best combination of efficacy and lack of toxicity. At the present time, no data support the efficacy of more than four to six cycles of chemotherapy. Increasing dose intensity above standard results in increased toxicity and is not currently supported. Therefore, at the present time, either concurrent or alternating chest radiation therapy with chemotherapy is preferred in patients with limited-stage disease. No evidence indicates that prophylactic cranial irradiation improves survival, but it is associated with increased central nervous system morbidity. The addition of radiation therapy does not seem to increase survival, but it does increase toxicity. Radiation therapy is used as palliation in patients in whom initial chemotherapy fails. This rare subset of patients has a 5-year survival of 50 to 70% if treated by surgery followed by chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy.
The syndrome must therefore be distinguished from prerenal azotemia by an empirical fluid challenge (1000 mL saline) or measurement of pulmonary wedge pressure medications in checked baggage order rulide canada. Other likely causes of renal failure must be excluded symptoms of breast cancer buy cheap rulide 150 mg online, such as acute tubular necrosis or renal impairment from aminoglycosides and contrast agents, although these typically lead to high sodium excretion. The prognosis of hepatorenal syndrome is very poor, in part because onset of the syndrome denotes end-stage liver disease. The most effective treatment for hepatorenal syndrome is to correct the underlying liver disease, by liver transplantation if appropriate. Treating any underlying infections and optimizing volume status are important adjunctive measures. Broad defects in protein synthesis and/or secretion characterize the cirrhotic liver. Clinically apparent defects include hypoalbuminemia, which can reduce oncotic pressure and accentuate edema formation, and reduced concentrations of plasma clotting factors. Thrombocytopenia can result from bone marrow hypoplasia induced by alcohol or due to hypersplenism associated with splenomegaly in portal hypertension. Platelet sequestration by the congested spleen often leads to significant thrombocytopenia, yet clinically significant bleeding almost never occurs; platelet transfusions are therefore not indicated in this setting unless there is an additional platelet defect. Similarly, portacaval decompression or splenectomy is usually curative but is not appropriate unless required to manage variceal hemorrhage. Hepatopulmonary syndrome refers to the triad of liver disease, pulmonary vascular dilation, and reduced arterial oxygenation. Although marked manifestations of the syndrome are unusual in patients with chronic liver disease, more subtle abnormalities of oxygenation are common. The abnormalities have been attributed to right-to-left shunts through pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas and development of bronchial varices in association with pulmonary hypertension. The syndrome occurs in chronic liver disease of all types and is more common in those with severe liver disease. As a result, the prognosis is poor, on the basis of both the pulmonary and hepatic disease. Affected patients complain of exertional dyspnea, with pulmonary function tests demonstrating normal lung volumes but markedly reduced diffusing capacity. Resolution of the syndrome has been seen in many patients after liver transplantation. Feminization in men with end-stage cirrhosis is particularly common in alcoholics and has been associated with increased estrogen and diminished testosterone levels. Altered drug metabolism (see Chapter 148) is an important consideration in prescribing drugs to those with end-stage liver disease, either because of impaired clearance leading to enhanced activity or toxicity, reduced sulfoxidation, or decreased protein binding. Bone disease manifested as thinning and spontaneous fractures is a major complication of late-stage cholestatic or alcoholic liver disease, especially primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatic osteodystrophy can be due to osteoporosis (see Chapter 257), osteomalacia (see Chapter 263), or both. Hepatocellular carcinoma (see Chapter 156) is often preceded by cirrhosis, which is usually but not always clinically apparent. Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P: Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. A thorough analysis of currently accepted criteria for diagnosis, clinical features, and therapy of alcoholic liver disease, including transplantation. The best long-term data to date showing a beneficial effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis. Variceal Hemorrhage Rossle M, Haag K, Ochs A, et al: the transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. This conclusion remains controversial, as outlined in an accompanying editorial (p. A review of data implicating nitric oxide as a potential mediator of metabolic derangements associated with ascites formation.
Purchase rulide discount. Ulrika Jonsson's Menopause Symptoms Made Her Fear Her Depression Had Returned | Lorraine.