"Order vasodilan cheap online, arteria costa rica".
By: Z. Sigmor, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Program Director, University of Minnesota Medical School
Findings are presented across categories of race or ethnicity unless otherwise indicated hypertension of pregnancy buy cheap vasodilan online. Finally hypertension with ckd best buy vasodilan, we consider how these perceptions can inform minority participation in genomics research that aims to improve health equity. Respondents often used physical characteristics, such as differences in body type and hair texture, as evidence of genetic variation. Participants understood genetics as being related to traits that are passed down through families and that contribute to physical characteristics, frequency of disease, and predisposition to disease. Genetics is viewed as being largely unchangeable and leading to inevitable health outcomes, and it is credited with being the reason why family members often experience the same health condition. One Latino male leader described genetics as follows: Genetics is an inheritance from your family. And diseases too, because they say "my grandmother had heart disease, my grandfather had diabetes," and you end up getting it until the third or fourth generation. Race and ethnicity were described as being associated with differing cultural norms and behaviors and with the creation of differential conditions under which genetic expression occurs. Racial and ethnic groups were often described as differing in diet and levels of physical activity, both of which were said to contribute to differences in disease outcomes. Diet included the type and amount of food consumed and how food is prepared; African Americans and Latinos were perceived as choosing less healthy food items and preparation techniques. A white lay female participant offered her perception of how dietary differences contribute to differential health outcomes: I think we are all predisposed to certain diseases based on your race. Genetics was seen as a key factor contributing not only to health outcomes but also to differences in predisposition across racial and ethnic groups. One African American male leader described this contribution by saying, "Genetics plays a large part in it. Participants acknowledged that there are variations in disease outcome by racial or ethnic group; however, respondents only discussed disease differences that exist for racial and ethnic minorities, and all but one of the examples given were for disparities experienced by African Americans. Although this perception was present for all 3 respondent groups, the proportion of respondents indicating that genetic differences are an underlying cause for differences in disease outcomes was nearly twice as great among white respondents as among African American or Latino respondents. Participants were familiar with the concept of genetics; however, there was an overwhelming lack of familiarity with the term genomics. Most participants (84% of African American respondents, 81% of white respondents, and 76% of Latino respondents) had not heard of the term. These social determinants included differential access to health care, education, fiscal resources, and even healthy food options. Latino respondents also cited language as a cause for differences, specifically in health outcomes, due to the inability of nonEnglish speakers to access adequate or appropriate health care and challenges in communicating with health care providers. One African American male leader described the situation as follows: I think that by way of people not being in the same economic playing field as a lot of other ethnic groups, by them not having access because of economics, it leads people not to get early treatments, which leads to the progression of certain diseases, or getting a further developed disease that someone with insurance was able to get early treatment and be treated for certain things. Interactions between genes and the environment were also described as creating racial and ethnic differences in gene expression based on where groups live, including both the physical living conditions and how "place" affects accessibility to health-promoting services. Their health is going to be better, their health is not going to decline as fast as the ones who is not getting those same things. African Americans were viewed as being more likely to live in conditions that exacerbate the expression of existing genetic predispositions to poor health outcomes. These living conditions were said to include the presence of toxins, insects, and proximity to industrial waste. I would think that would have an effect on diseases and whether they may carry a genetic trait, but because of some of those disparities they may not be able to prevent them as best they could if they were in a more healthy environment. Not surprisingly, most African American and Latino respondents indicated concerns about research that aims to address health disparities (88% and 86%, respectively); however, most white respondents (81%) also cited concerns. Among those with concerns, the proportion of respondents whose concerns were directly tied to race was nearly twice as great among African American and Latino respondents as among white respondents. African Americans and Latinos spoke of mistrusting researchers and the government; these individuals also spoke of fearing medical abuses, the use of research to "promote" one race over another, genocide, and mistreatment or targeting of a particular race.
Certain proteins that bind tightly to methylated CpG sequences form complexes with other proteins that act as histone deacetylases pulse pressure sites buy cheap vasodilan 20mg on-line. In other words arrhythmia 1 cheap vasodilan 20 mg with amex, methylation appears to attract deacetylases, which remove acetyl groups from the histone tails, stabilizing the nucleosome structure and repressing transcription. In some cases, the molecular basis of these effects is at least partly understood. Epigenetic changes induced by maternal behavior A fascinating example of epigenetics is seen in the longlasting effects of maternal behavior in rats. Mother rats lick and groom their offspring, usually while the mother arches her back and nurses the offspring. The offspring of mothers who display more licking and grooming behavior are, as adults, less fearful and show reduced hormonal responses to stress compared with the offspring of mothers who lick and groom less. To demonstrate the effect of altered chromatin structure on the stress response of the offspring, researchers infused the brains of young rats with a deacetylase inhibitor, which prevents the removal of acetyl groups from the histone proteins. This research suggests that identical twins do differ epigenetically and that phenotypic differences between them may be caused by differential gene expression. Additional examples of epigenetic effects include genomic imprinting (discussed in Chapter 5) and X-chromosome inactivation (discussed in Chapter 4). Molecular Mechanisms of Epigenetic Changes Epigenetics alters gene expression, alteration that is stable enough to be transmitted through mitosis (and sometimes meiosis) but that can also be changed. Most evidence suggests that epigenetic effects are brought about by physical changes in chromatin structure. The fact that epigenetic marks are passed on to other cells and (sometimes) to future generations means that changes in chromatin structure associated with epigenetic phenotypes must be faithfully maintained when chromosomes replicate. Immediately after semiconservative replication, the cytosine base on one strand (the template strand) will be methylated, but the cytosine base on the other strand (the newly replicated strand) will be unmethylated (Figure 17. How histone modifications, nucleosome positioning, and other types of epigenetic marks might be maintained across replication is less clear. One possibility, discussed in Chapter 12, is that, after replication, the epigenetic marks remain on the original histones, and these marks recruit enzymes that make similar changes to the new histones. Epigenetic effects caused by prenatal exposure In another study, researchers found that the exposure of embryonic rats to the fungicide vinclozolin, which reduces sperm production, led to reduced sperm production not only in the treated animals (when they reached puberty), but also in several subsequent generations. This study and others have raised concerns that, through epigenetic changes, environmental exposure to some chemicals might have long-lasting effects on the health of future generations. Epigenetic effects in monozygotic twins Monozygotic (identical) twins develop from a single egg fertilized by a single sperm that divides and gives rise to two zygotes (see Chapter 6). The nature of these differences in the phenotypes of identical twins is poorly understood, but recent evidence suggests that at least some of these differences may be due to epigenetic changes. Furthermore, these dif- the Epigenome the overall pattern of chromatin modifications possessed by each individual organism has been termed the epigenome. As a stem cell divides and gives rise to a more specialized type of cell, the geneexpression program becomes progressively fixed so that each particular cell type expresses only those genes necessary to carry out the functions of that cell type. In mammals, most methylation is at cytosine bases, converting cytosine into 5-methylcytosine. The researchers identified the location of 5-methylcytosine across the entire genome in two cell types: (1) an undifferentiated human stem cell; and (2) a fibroblast, a fully differentiated connective tissue cell. The researchers found widespread differences in the methylation patterns of these two types of cells. The epigenome is the genomewide pattern of epigenetic changes possessed by an individual organism. Most act by stimulating or stabilizing the assembly of the basal transcription apparatus. The basal transcription apparatus is capable of minimal levels of transcription; transcriptional regulator proteins are required to bring about normal levels of transcription. These proteins bind to a regulatory promoter, which is located upstream of the core promoter (Figure 17.
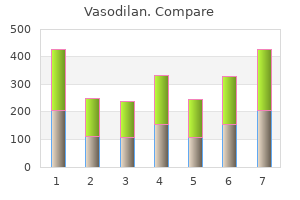
It is water soluble heart attack people vasodilan 20 mg, well absorbed by mouth even in infancy and largely excreted unchanged in the urine blood pressure 9870 order vasodilan discount. While high-dose systemic exposure (400 mg/day) in the first trimester of pregnancy can produce a constellation of serious fetal abnormalities, there are, as yet, no reports of teratogenicity with a single 150 mg dose in the first trimester or with topical or oral use later in pregnancy. Studies suggest that it is less toxic and at least as effective as amphotericin B. Liver function tests sometimes show a mild self-correcting disturbance, and rashes can occur, but serious drug eruptions have only been seen in immunodeficient patients. There is no good reason to give amphotericin B as well as high-dose fluconazole, but there is evidence that effective treatment of all Candida species with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 8 micrograms/ml requires a higher dose than many reference texts currently quote (Wade et al. In vitro modelling also suggests that high-dose treatment makes the emergence of resistant strains less likely. Oral fluconazole is widely used to treat superficial (topical) infection in adults and is now starting to be used for this purpose in babies. Prophylactic use has been widely studied in the last ten years (see web commentary), but some prefer to use nystatin (q. Diagnosing systemic candidiasis Systemic candidiasis is difficult to diagnose, but not rare in colonised ill babies. Unfortunately, blood cultures may take days to reveal evidence of infection and can be misleadingly negative. The presence of budding yeasts or hyphae in freshly voided urine should lead to an immediate search for further evidence of infection. A suprapubic tap can be used to collect urine for microscopy and fungal culture to clinch any diagnosis and prove that treatment has been effective. Give the mother a 150300 mg loading dose by mouth and then 100200 mg once a day for at least 10 days. Treat the baby as well, and take steps to minimise the risk of reinfection as outlined in the web commentary. Age under 2 weeks: Give 6 mg/kg of fluconazole on day 1 and then a further 6 mg/kg every third day. Age 24 weeks: Give 6 mg/kg of fluconazole on day 1 and then a further 6 mg/kg every second day. Candida infection of the breast Prophylactic use in the neonate Treatment of invasive candidiasis Age under 2 weeks: Give 612 mg/kg of fluconazole every third day. A loading dose of 25 mg/kg has sometimes been recommended and shortens the time to achieving therapeutic levels. A powder for oral use which, when reconstituted, provides 35 ml of a 10 mg/ml solution costs Ј16. Reducing Candida infections during neonatal intensive care: management choices, infection control, and fluconazole prophylaxis. Fluconazole dosing for the prevention or treatment of invasive Candidiasis in young infants. This combination is used to treat aspergillosis, coccidioidomycosis and cryptococcosis and is also often used to treat systemic Candida infection, although many now prefer to use fluconazole (q. Pharmacology Flucytosine (previously called 5-fluorocytosine) is a fluorinated pyrimidine first developed in 1957 which acts as a competitive inhibitor of uracil metabolism. The drug is well absorbed by mouth and more than 90% is excreted unchanged in the urine. While flucytosine has been used on its own to treat Candida renal tract infection, resistant strains have been reported. Co-treatment with either amphotericin or fluconazole is now universally recommended to reduce the emergence of drug resistance. Because co-treatment with amphotericin and the underlying fungal infection can both cause renal impairment, monitoring the trough blood level is important if the plasma creatinine level exceeds 40 mol/l. Vomiting and diarrhoea can occur, and reversible liver function changes have been reported. Flucytosine has been given in pregnancy without seeming to cause any apparent harm to the baby, but the risk of teratogenicity cannot be discounted (in part due to its conversion to 5-fluorouracil). The manufacturers also recommend slow infusion over at least 20 minutes, although they offer no reason for this recommendation. Older children: A dose of 50 mg/kg every 6 or 8 hours is normally used in older children.
Buy discount vasodilan 20 mg online. Panasonic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitoring Device.
Light is not required prehypertension stage 2 purchase vasodilan with a mastercard, however blood pressure 7843 cheap vasodilan online visa, for the appearance of gills and subsequent growth and expansion to the mature fruiting body stage, but the functioning of the fruiting body by production of spores ceases if the fruiting body is placed in the dark. A period of light of 5 to 6 hours is then required for recovery from the dark inhibition of sporulation (Figure 7. The opposite extreme of a requirement for light for fruiting body formation is that of inhibition by light. In some species, of which Agaricus bisporus is the best-known example, light is inhibitory to the development of fruiting body primordia and also has been demonstrated to inhibit stipe elongation and pileus expansion. There are a number of fungi that require light for the normal development of the fruiting body. In the ascomycete Sordaria fimicola, perithecia are produced in both light and darkness, but the perithecia produced in darkness are smaller. In the basidiomycete Flammulina velutipes, light is required for the normal expansion of the pileus. The studies of Plunkett22 indicate an effect of light for pileus expansion of Polyporus brumalis similar to that just mentioned for F. Kitamoto and co-workers10-13 have reported on a series of studies dealing with the details of the effects of light on pileus formation in Favolus arcularius. In this basidiomycete, pileus formation is induced by light, as is also true for Panus fragilis and Boletus rubinellus. A technique was developed that permitted synchronous pileus formation so that the effect of light on the initiation of pileus formation could be studied. The method was to use stipes (lacking pilei) which had been preincubated in darkness for 48 to 72 hours. It was found that pileus formation then would begin about 24 hours after the start of illumination, but constant illumination was not required; pileus formation occurred if a dark period was interposed between 1 and 8 hours after the start of illumination. The initiation of pileus formation was discovered to involve two light-requiring steps: the first, which occurred during the first hour of illumination, was saturated with 5 lux of light, and the second light process caused earlier pileus-primordium formation the more the light intensity was increased up to 150 lux. Phototropism is a growth response that causes a bending toward (positive) or away from (negative) light. Although the studies of the phototropic response of the sporangiophore of Phycomyces are classical, our present concern has to do with phototropism in relation to the development of fruiting bodies of basidiomycetes. Earlier in the chapter we mentioned that one of the roles of the mushroom is to provide for effective dissemination of the spores that are produced on the basidia. Phototropism plays a prominent role in spore dissemination in many basidiomycetes. Basidiospores are forcibly ejected from the basidium by a discharge mechanism that involves the bursting of a bubble that forms near the point where the basidiospore is attached to the sterigma (Figure 7. The basidiospores are only discharged a short distance by this method, but it is a distance sufficient to place the spore in a position that, when the forces of gravity take over, permits the spore to fall free of the hymenial surface ж provided that the gills of the agaric or tubes of the polypore are properly aligned by the positioning of the stipe and pileus. This, then, is accomplished to an extent by phototropic responses in the stipes of a number of mushrooms, including species of Coprinus, Flammulina velutipes, Polyporus brumalis, and many other species, including Schizophyllum commune. The mushroom then grows in response to negative geotropism; however, if the source of light is changed to come from a direction not shielded by the pileus so that it falls on the stipe, the positive phototropic response takes over. In nature, both phenomena operate to provide a proper orientation of the fruit body for basidiospore dissemination. Studying a stipitate mutant, they found that the stipe was not affected by gravity. However, the apical pit stage was found to be positively geotropic, and the next stage, involving development of the gills, was also found to occur in response to gravity, with the gilled surface becoming oriented to face downward. Hawker7 wrote, "The total amount, nature, and concentration of food materials necessary for reproduction may all be different from those favoring vegetative growth. Let us first consider the effect of concentration of nutrients on the fruiting process. Is this to be interpreted as indicating that fruiting will not occur so long as vegetative growth is taking place? Does it mean that exogenous nutrients are not required for mushroom production once the fruiting body primordia have been initiated? Studies of Kitamoto and co-workers,10,11 using replacement cultures for studying the nutritional requirements of fruiting body formation of Favolus arcularius, found that the main source of nutrients for growth of the mushrooms was the vegetative mycelial cells, but that some nutrients for growth of the mushrooms were also obtained directly from the medium. Studies of fruiting body formation of a similar nature involving Psilocybe panaeoliformis were also reported from the laboratory of Kitamoto.
Alfalfa hay with 65% dry matter was chopped in 3 cm size and ensiled using 3 different varieties of waste dates (Berin arrhythmia questions buy vasodilan 20 mg low price, Ghybani blood pressure medication green pill buy generic vasodilan 20 mg on-line, Amobahri) in different levels 0, 6, 12 and 18%. Air-stability of alfalfa silage including of waste date increased significantly (P < 0. Appearance evaluation was shown that calculated score of smell, structure and color of alfalfa silages with 12 and 18% of all varieties of waste dates was 20 (very good rank), alfalfa silage with 6% of all varieties of waste dates was 18 (good rank) and alfalfa silage without the addition of waste dates was 16 (acceptable rank). After treatment, about 1 kg of forage was packed into 5 individually replicated nylon-polyethylene vacuum barrier bags for each treatment. Harvesting occurred at early-dent and 1/2 milk-line stages of maturity during years 1 and 2, respectively. The model included the fixed effects of year, field, hybrid, planting density, and all their interactions. Key Words: corn, plant population, phosphorus T88 Effects of feeding two different types of sorghum-sudangrass silage based diets on nutrient intake and digestibility and growth of Holstein dairy heifers. Pregnant dairy heifers can overconsume energy when fed diets with lower fiber levels causing higher intakes. The 3 diets were randomly allocated to the pens within each block and offered for 12 weeks. There were no differences on performance or health among the different colostrum feeding protocols. Key Words: health, IgG, newborn T90 Performance and diarrhea occurrence of suckling calves supplemented with colostrum replacer. The importance of colostrum for the survival of neonatal calves and its consequences on their productive and reproductive life has been known for many years. Calves assigned to the control group received 6 L of milk 3 times daily without colostrum inclusion. Even the number of cases of diarrhea almost doubled in non-supplemented calves (13/7), diarrhea occurrence was not significantly different among calves from the treatment and control groups (P = 0. Key Words: calf weight, immunoglobulin G, weaning T91 Effect of feeding transition milk on growth and health of dairy calves. After treatments were complete at 4 d of age, calves were fed and managed similarly. Body weights, blood samples and daily health scores (scale of 0 to 3) were collected through weaning at 56 d of age. All but one calf achieved successful passive transfer of immunity with serum IgG values over 10. Key Words: transition milk, calf T92 Prenatal choline supplementation programs the metabolome of the fetus after birth. This is a polar embedded stationary phase that provides comprehensive coverage, but does have some limitation is the coverage of very polar species. A total of 7745 molecular features were detected of which 356 peaks with putative identification represent 305 unique metabolites, including amino acids, benzoic acids, lipid molecules, carbohydrates, purines, pyrimidines, vitamins, and other intermediate and secondary metabolites. Further data analyses are needed to unravel the specific consequences of these changes. In mature ruminants, B vitamins are produced by rumen microbes but the newborn calf relies on placental and colostral transfer of the vitamins to cover its requirements. The study was conducted to evaluate biotin (B8), folates (B9) and vitamin B12 (B12) concentrations in colostrum of cows receiving vitamin supplements and in plasma of their calves fed with their colostrum. Supplementary B9B12 increased colostrum B9, from 673 to 1,094 ± 52 ng/mL, colostrum B12, from 29 to 58 ± 3 ng/mL, calf plasma B9 from 16 to 30 ± 2 ng/mL (P < 0. Further studies are needed to evaluate if the increase in calf birth weight when a B9B12 supplement was given to cows in late gestation could be due to an epigenetic effect as reported for other species. Key Words: lipolysis, transition cow, fatty liver T96 Actions of recombinant bovine somatotropin revisited: Characterization of the plasma metabolome and lipidome. Eight Holstein cows were blocked by parity and assigned to one of 4 Ч 4 Latin squares balanced for carryover effects with a 2 Ч 2 factorial arrangement of treatments.