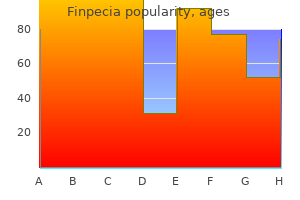
"Trusted finpecia 1mg, hair loss gluten".
By: S. Tjalf, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Professor, University of Pikeville Kentucky College of Osteopathic Medicine
Our instrument was a binary variable indicating treatment initiation occurred during service interruption hair loss upset stomach order genuine finpecia on-line. Cancer stage was considered ordinal and we used Poisson regression to calculate weeks for stage progression hair loss medication wikipedia order 1 mg finpecia amex. Results: A total of 301 cervical cancer cases were included with 138 (46%) exposed to service disruption and 163 (54%) not exposed. Conclusion: Stage progression is rapid in locally advanced cervical cancer with typical treatment delays of two months associated with a full stage increase. Aim: To identify patient and visit characteristics associated with missing appointments, and describe reasons for missed visits among adult patients undergoing evaluation for possible cancer at public facilities in a rural district in Botswana. Methods: Patients $ 18 years with symptoms or signs suggestive of cancer were enrolled in the Potlako trial, an ongoing prospective health systems pilot seeking to improve timely diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Study staff tracked patient visits and if a patient missed a visit, study staff administered a brief structured phone interview to 1) determine reasons, 2) reschedule visit and 3) arrange transport support if needed. Patients who enrolled and completed follow-up between May 1, 2016 and March 23, 2018 were included in analysis. Conclusion: Multiple visits are required to complete evaluation for cancer suspects and missed visits are common. Our findings suggest possible interventions to improve efficiency, which include: simplifying diagnostic cascade, transport support, visit reminders, intensified counseling for younger patients and those seen at general outpatient clinics, and avoidance of Friday scheduling. Oluwole University of Abuja, Department of Pathology/Forensic Medicine, Abuja, Nigeria Background: the incidence of prostate cancer (Pca) is the first in malignant tumors among men in the United States, and mortality rate is the second cause of deaths. Incidental prostate cancer is defined as clinically inapparent tumor that is neither palpable nor visible by imaging. Aim: To identify incidentally detected prostate cancer in benign prostatic specimens submitted for histopathology Methods: this is a ten-year retrospective histopathology study of all prostate cancer cases diagnosed between 1991-2000 in the department of Pathology, Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital, Zaria, Nigeria. Two patients in their fourth decade were found to have incidental prostate cancer. Heyworth Gold Coast University Hospital, Medical Imaging, Gold Coast, Australia Background: the tissue diagnosis of lymphoma and metastases is commonly obtained from affected lymph nodes. The lymph nodes chosen for biopsy are often the consequence of their appearance on ultrasound, which determines their risk of malignancy. The project also reviewed the role of clinical experience in both the choice of sampling technique and diagnostic yield. Methods: Retrospective study of percutaneous lymph node biopsies performed at a large tertiary hospital between July 2016 and March 2018. The associated ultrasounds were reviewed and the lymph nodes were classified as high or low risk of malignancy by their sonographic appearance. The diagnostic yield was then separately assessed for lymph nodes of high and low malignant potential. The effect of clinical experience on diagnostic yield was also examined, by comparing the outcomes of radiology consultants and radiology trainees. Results: 296 lymph node biopsies were reviewed and statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression analysis. Biopsies obtained by radiology trainees provided a diagnosis twice as often as those obtained by radiology consultants. However, the feasibility and clinical role of diagnostic ultrasound in such settings has not been described. Patient diagnoses and follow-up were extracted from medical records using a standardized data collection form. Of those recommended for biopsy at initial presentation, 151 (96%) had a biopsy at that time. As of November 23, 2017, all patients ultimately diagnosed with cancer had had a biopsy at their initial visit, and no patients who had been discharged or recommended for clinical or radiographic surveillance had been subsequently diagnosed with cancer. Clinical follow-up and evaluation are ongoing to assess longer-term patient outcomes, cancer detection rates among patients who are not initially biopsied, and rates of follow-up among patients recommended to have clinical or radiographic surveillance. Conservative management of low-risk breast cancer may reduce the harm of overdiagnosis resulting from mammographic screening programs, yet little is known about how such strategies might impact upon quality of life. Demographics and a history of prior screening participation or breast cancer diagnosis were examined as predictors of screening and treatment pathway preferences.
Psychologically oriented pain therapists cannot have a naive attitude toward the pain and neglect somatic causes hair loss 4 months postpartum discount generic finpecia uk, because otherwise hair loss updates purchase finpecia 1mg mastercard, patients with mental disorders. Interdisciplinary teams, with a biopsychosocial treatment concept, do not distinguish between somatic and the psychological factors, but treat both simultaneously within their individual specialties and through consultation with one another. Psychological pain therapy Psychological interventions play a well-established role in pain therapy. They are an integrative component of medical care and have also been successfully used for patients with somatic disorders. Together with psychotherapeutic techniques, they can be used as an alternative or an addition to medical and surgical procedures. Patients with chronic pain usually need psychological therapy, because psychosocial factors play a crucial role in the chronicity of pain and are also a decisive factor in terms of enabling the patient to return to work. The interventions may be used within the context of various therapies and require different levels of psychological expertise, as shown in Table 1. Due to the strong focus on physical processes, certain processes such as biofeedback and physical and psychological activation are particularly well received by many patients. Patients with chronic pain often feel incapable of doing something about their pain themselves. Due to many failed therapies, they have become passive and feel hopeless and depressed. Acceptance does not equal resignation, but allows for: · Not giving up the fight against pain, · A realistic confrontation of the pain, and · Interest in positive everyday activities. The most important psychological therapies are based on the principles of the theory of learning and have led to the following rules: · Let the patient find out his or limits with regard to activities such as walking, sitting, or climbing stairs, with no significant pain increase. Behavioral processes are geared toward changing obvious behaviors such as taking medication and using the health care system, as well as other aspects relating to general professional, private, and leisure activities. They focus particularly on passive avoidance behaviors, a pathological behavior showing anxious avoidance of physical and social activity. This step is accompanied by extensive education initiatives that help reduce anxiety and increase motivation to successfully complete this phase. The goal of therapy is to reduce passive pain behavior and to establish more active forms of behavior. The therapy begins with the development of a list of objectives that specify what the patient wants to achieve. These objectives must be realistic, tangible, and positive; complex or more difficult objectives can be addressed successively, and unfavorable conditions must be carefully taken into consideration. It does not make sense to encourage a patient to return to work and to make this an objective if this is unlikely, due to the conditions on the job market. A better therapy objective might be to achieve better quality of life by getting involved in meaningful leisure activities. The support patients receive in therapy makes it more likely that they will continue 22 Table 1 Psychological interventions and therapy targets Intervention Patient training Therapeutic Targets Treatment Context Harald C. Analyze conditions that increase pain and stress General medicine Psychologist + physiotherapist General medicine Physician + psychologist/psychiatrist Handling of medications Relaxation training Resource optimization Activity regulation ++ + + ++ Pain and coping Involvement of caregivers Improvement of self-observation Psychologist/psychiatrist General medicine Psychologist/psychiatrist ++ + +++ Stress management Learning how to enjoy activities Communication Developing perspectives for the future Special Therapies Cognitive restructuring Biofeedback Learn systematic problem-solving Psychologist/psychiatrist tools and how to cope with stress Strengthen activities the patient enjoys and likes to do Change inadequate pain communication and interaction Develop realistic perspectives for the future (professional, private) and initiate action plans Modify catastrophizing and depressive cognitions Learn how to activate specific motor and neuronal (vegetative and central nervous) functions and learn better self-regulation Restore private and professional functionality; reduce subjective impairment perception and movement-related anxiety General medicine/physiotherapist General medicine or psychologist General medicine +++ + + + Psychologist/psychiatrist Psychologist +++ ++++ Functional restoration Interdisciplinary: orthopedic physician + ++++ physiologist * Low (+) to high (++++). Often, however, therapists must not only encourage activities, but also plan phases of rest and relaxation to make sure patients do not overly exert themselves. Cognitive-emotional modification strategies, on the other hand, predominantly focus on changing thought processes (convictions, attitudes, expectations, patterns, and "automatic" thoughts). These are various techniques that teach patients a new, more appropriate set of cognitive (and behavioral) skills to help them cope with pain and limitations. Patients are taught, for example, how to identify thoughts that trigger and sustain pain, how to perceive situational characteristics, and how to develop alternative coping strategies. If patients are taught appropriate coping techniques, they are better able to control a situation; new confidence in their abilities leads to a decrease in feelings of helplessness, and patients become more proactive. One of the goals of therapy is for patients to learn to monitor the function of expressing symptoms (something patients are usually not aware of) to be able to better manage and manipulate their social environment. During the course of this analysis, patients and their therapists systematically collect information on how internal or external events are connected to the pain experience and pain behavior.
Transposition of the great arteries the aorta is connected to the right ventricle hair loss cure in 2 years purchase finpecia 1 mg visa, and the pulmonary artery is connected to the left ventricle (discordant ventriculoarterial connection) hair loss cure breakthrough order cheapest finpecia and finpecia. Echocardiography this is essential to demonstrate the abnormal arterial connectionsandassociatedabnormalities. Common mixing (blue and breathless) Theseinclude: · Atrioventricularseptaldefect(complete) · Complexcongenitalheartdiseasee. Gradually, those children that survive, become less symptomatic, as the shunt decreases. Atrioventricular septal defect (complete) Thisoccursin: · Atrioventricularseptaldefect(complete) · Complexcongenitalheartdisease this is most commonly seen in children with Down syndrome. Complex congenital heart disease Itisdifficulttogeneraliseabouttheseconditions,(tri cuspidatresia,mitralatresia,doubleinletleftventricle, commonarterialtrunktruncusarteriosus)sincetheir mainpresentingfeaturedependsonwhethercyanosis orheartfailureismorepredominant. Completely corrective surgery is not possible with most, as there is often only one effective functioning ventricle. Management In children, regular clinical and echocardiographic assessmentisrequiredinordertoassesswhentointer vene. Most neonates and children with significant aortic valvestenosisrequiringtreatmentinthefirstfewyears oflifewilleventuallyrequireaorticvalvereplacement. Early treatment is therefore palliative and directed towardsdelayingthisforaslongaspossible. Intheneonatalperiod,thosewithcriticalaorticste nosis and a ductdependent systemic circulation may presentwithsevereheartfailureleadingtoshock. When the duct closes, the aorta also constricts, causing severeobstructiontotheleftventricularoutflow. Iftheydopresentafterbirth,theyarethesickestofall neonates presenting with a ductdependent systemic circulation. Restricted exercise is advised only for children with severe residual aortic stenosisandforventriculardysfunction. The mostcommonreasonforthisisreplacementofartifi cialvalvesandreliefofpostsurgicalsuturelinesteno sis, for example recoarctation or pulmonary artery stenosis. Management In the severely ill child, prompt restoration of sinus rhythmisthekeytoimprovement. Thisisachievedby: · Cardiac arrhythmias Sinusarrhythmiaisnormalinchildrenandisdetectable as a cyclical change in heart rate with respiration. Those who relapseorareatriskareusuallytreatedwithpercutane ous radiofrequency ablation or cryoablation of the accessorypathway. There is rarely a structural heart problem, but an echocardiogram should be performed. This antibody appearstopreventnormaldevelopmentoftheelectri cal conduction system in the developing heart, with atrophy and fibrosis of the atrioventricular node. It may cause fetal hydrops, death in utero and heart failure in the neonatal period. However, most remain symptomfree for many years, but a few become symptomaticwithpresyncopeorsyncope. Insusceptibleindividuals,there isanabnormalimmuneresponsetoaprecedinginfec tion with group A haemolytic streptococcus. Anyonewithafamilyhistoryofsuddenunex plained death, or a history of syncope on exertion shouldbeassessed. Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ectopic atrial tachy cardia, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrilla tion occur in children, but all are rare. Althoughthemitralvalve is the most frequently affected, aortic, tricuspid and, rarely,pulmonaryvalvediseasemayoccur. Syncope this is a common symptom in teenagers and usually doesnotrepresentcardiacdisease. Alternatively, the penicillin can be given orally every day, but compliance may be a problem. Most recommendtreatmenttotheageof18or21years,but, more recently, lifelong prophylaxis has been advo cated. Thepresence of the classical peripheral stigmata of infective endo carditisshouldnotbereliedupon.
Finpecia 1 mg on-line. Alopecia Wigs Wigs for Cancer Hair Loss Treatment Cure | Custom Designed | Human Hair Wigs.
B: the corresponding axial plane at the level of the pelvis at 12 weeks of gestation showing the presence of a keyhole sign hair loss cure march 2013 order 1mg finpecia amex, suggesting a posterior urethral valves hair loss 2016 purchase finpecia online now. C: the follow-up ultrasound at 14 weeks of gestation showing resolution of the megacystis with a longitudinal bladder diameter of 6 mm. D: An axial plane of the pelvis in color Doppler at 18 weeks of gestation showing normal bladder and umbilical arteries with no bladder wall hypertrophy, as evidenced by the proximity of the umbilical arteries to the internal bladder wall (arrows). Urethral atresia on the other hand occurs in males and females and is extremely rare. Ultrasound Findings Megacystis is probably the easiest and most commonly diagnosed abnormality of the genitourinary system in the first trimester. It is based on the identification of a large bladder, measuring 7 mm or more in sagittal view. In some cases of resolving megacystis, a thickened bladder wall may still be observed. The presence of progressive obstructive uropathy is common when the longitudinal bladder length measures greater than 15 mm. B: A parasagittal plane of the same fetus at 13 weeks of gestation demonstrating a normal bladder size and echogenic bladder wall. C: An axial plane of the pelvis at 13 weeks of gestation showing bladder wall hypertrophy, with bladder wall thickness of 1. D: An axial plane of the pelvis in color Doppler at 13 weeks of gestation confirming the presence of bladder wall hypertrophy as evidenced by the distance between the umbilical arteries and the internal bladder wall (double headed arrow). This finding is associated with significant risk for aneuploidy and renal abnormalities. Amniotic fluid appears normal in all fetuses, as expected in the first trimester in the presence of significant uropathy, and oligohydramnios is not expected before 16 weeks of gestation. Follow-up ultrasound examinations often demonstrate the presence of renal abnormalities and underdeveloped lungs, expected here in fetuses B, C, and D because of significant megacystis with abdominal wall distention. In B, the anterior abdominal wall and bladder were opened digitally using postprocessing volume cutting tools to provide an insight into the dilated bladder. C: Postprocessing with transparency tool (silhouette ), thus facilitating the visualization of the megacystis. In this case, it is not feasible to relate the presence of increased renal parenchyma echogenicity to urologic obstruction or trisomy 13. Associated Malformations Megacystis in the first trimester has been associated with chromosomal malformations, primarily trisomy 13 and 18. In a recently published large study on 108,982 first trimester fetuses including 870 fetuses with abnormal karyotypes, megacystis was found in 81 fetuses for a prevalence of 1:1,345. The rate of aneuploidy in megacystis was 18% (15/81) and, in this study, was similar in both subgroups. Note the presence of a massively distended bladder (megacystis) in A and B and a keyhole sign (circle in B) typical for the presence of urethral obstruction. The renal pelvis is considered normal when it measures <4 mm at <28 weeks gestation and <7 mm at >28 weeks gestation. It is important to note, however, that these features are difficult to assess in the first trimester, and several may not be evident until the second or third trimester of pregnancy. A close follow-up in the second trimester is thus recommended to document any progression or resolution. Postprocessing volume cutting is performed in A and B to display the dilated bladders (asterisks). Note the keyhole sign in fetus B, suggesting the presence of posterior urethral valves. Transvaginal ultrasound was performed (C and D) to better assess the urogenital organs. Neither a keyhole sign nor abnormal kidneys were found, and the cystic structure was noted to be located in the middle right abdomen under the liver and cranial to a small bladder (C). Color Doppler confirmed the presence of a small filled bladder, normally located between the two umbilical arteries, as shown in D. The corresponding orthogonal coronal view in B shows that the cystic structure (asterisk) is located laterally in the right abdominal cavity and not midline as expected in megacystis.