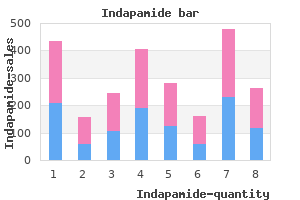
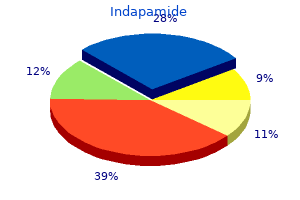
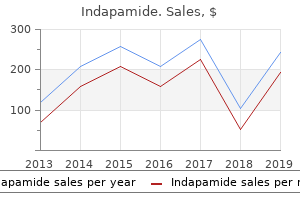
"Buy 2.5mg indapamide overnight delivery, hypertension lifestyle modifications".
By: Z. Malir, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Co-Director, Medical College of Wisconsin
The number of cases can vary by geographic location blood pressure variation during the day generic indapamide 2.5mg visa, and analysis by place can help identify where an increase in cases is occurring pulse pressure 16 discount 1.5mg indapamide visa. In the case of rare congenital anomalies, the size of the geographic unit to be considered is important in order to provide stable estimates. The analysis of demographic characteristics provides information on the characteristics of those individuals with particular congenital anomalies. The most frequently used demographic variables for analysis are age, sex, and race and ethnicity. Knowing only the number of cases (numerator data), without having information about the denominator, can result in a misinterpretation of the true burden of a congenital anomaly. Example of calculating prevalence and the importance of the denominator Numerator: total number of cases of congenital anomalies per year Country (example A) 100 Denominator 100 000 (total live births per year in region or total catchment area) 10 000 (total live births per year in eight hospitals of the total catchment area) 1000 (total live births per year in one referral hospital of the total catchment area) Prevalence 0. The surveillance programme will be population based and will include all fetuses or neonates identified with congenital anomalies in the region. Example B A country decides to start a congenital anomalies surveillance programme in all maternity hospitals in one region, and eight hospitals will participate. Only fetuses or neonates with congenital anomalies born in one of the eight participating hospitals will be counted. The total number of births per year in the eight hospitals is estimated to be 10 000. After one year, the programme identifies 100 fetuses or neonates with congenital anomalies. This hospital is where prenatally identified fetuses with congenital anomalies are usually referred for delivery. After one year, the hospital identifies 100 fetuses or neonates with congenital anomalies. Without knowing the denominator for each example, the prevalence estimate could be misinterpreted. The prevalence estimate for example C might indicate that this country has a high prevalence of congenital anomalies, when in reality the estimate resulted from a small denominator and the site is a referral hospital. The prevalence estimates for examples B and C represent the prevalence for eight hospitals and one referral hospital, respectively. The prevalence estimate for example A is based on the total number of live births for a population and, thus, it yields the most accurate prevalence estimate. Diagnosing and coding congenital anomalies Initial list of congenital anomalies to consider for monitoring Surveillance programmes can be developed to capture a variety of conditions. Although some countries may have more developed programmes than others, for the purpose of this manual, the following are suggested as an initial list of congenital anomalies to consider for monitoring. They were chosen because they are relatively easy to identify at birth, have significant public health impact, and, for some of them, the potential for primary prevention. However, high-quality data on a smaller number of congenital anomalies will be more useful for public health than poor-quality data on all congenital anomalies. It is important that decisions on which defects to include are evaluated based on available resources. If the fetus or neonate 41 has at least one eligible congenital anomaly, this and any other observable major and minor congenital anomalies are described in detail and included on the abstraction form (see Appendix G). When coding the congenital anomalies, it is important to be as specific as possible and avoid using codes that are nonspecific or too general. Congenital anomalies of the nervous system Neural tube defects affect the brain and spinal cord, and are among the most common of the congenital anomalies. The most prevalent types of neural tube defects are anencephaly, encephalocele and spina bifida. Neural tube defects Source: reproduced with permission of the publisher from Botto et al. In addition to the term anencephaly, two other terms are used, although rarely, to describe this anomaly. One is holoanencephaly, in which the bone defect extends through the foramen magnum, affecting the entire skull; in the other, meroanencephaly, the bone defect is limited to the anterior part of the skull.
Muntner has an extensive bibliography in clinical and population hypertension blood pressure medication gynecomastia generic 1.5 mg indapamide free shipping, including over 500 peer-reviewed journal articles pulse pressure youtube cheap 2.5mg indapamide fast delivery. As a clinician, he has broad activities in internal medicine and nephrology based at the universityaffiliated hospitals, where he was chief of the Department of Internal Medicine between 2010 and 2016, and the director of the residency program in nephrology from 2013 to 2016. He was a visiting scholar for extended periods at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and the George Institute in Australia. He has participated as a principal investigator, regional leader, and on steering committees in multinational clinical trials. Consultancy: Akebia, AstraZeneca, Fresenius Medical Care, and Novo Nordisk Grant/research support: Fresenius Medical Care* Speaker bureaus: AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk *Monies paid to institution. Sarnak has a long record of national and international leadership positions in nephrology. Sarnak is a previous recipient of a K24 Midcareer Career Award in Patient-Oriented Research and has mentored more than 20 research fellows and 9 junior faculty members. He has published more than 350 articles, including more than 85 peer-reviewed, non-review articles, with his mentee as the first author. His mentees now include professors of medicine and chiefs of divisions of nephrology at other institutions. Consultancy: Akebia*, Bayer, and Cardurion Pharmaceuticals Grant/research support: National Institutes of Health* *Monies paid to institution. Consultancy: AstraZeneca Grant/research support: Bayer* Speaker bureaus: AstraZeneca and Janssen *Monies paid to institution. His involvement in guideline development started with the third edition of the Renal Association Clinical Practice Guidelines. He was a Health Foundation Quality Improvement Fellow at the Institute for Healthcare Improvement in Boston from 2003 to 2004, a placement that led to a keen interest in the translation of evidence into reliable practice and in shared decision-making. Tobe trained in internal medicine and nephrology at the University of Toronto, Ottawa, Canada. He is a professor of medicine at both the University of Toronto and the Northern Ontario School of Medicine and the Nephrology Postgraduate Fellowship Director at the University of Toronto. Tobe was previously the director of the nephrology division at Sunnybrook Research Institute. His main research interests are implementation science for the dissemination of cardiovascular-focused clinical practice guidelines. Tobe serves on the Board of Directors of the American Society of Hypertension Specialists Program. Tobe has received many teaching awards and other career distinctions, has published over 150 peer-reviewed articles, and has led and participated in peer-reviewed, investigator-initiated, and multi-centered international research collaborations. Jadoul trained in internal medicine and nephrology under the mentorship of Professor Charles van Ypersele de Strihou. Jadoul has coauthored over 260 scientific papers, most of them published in major nephrology journals. Consultancy: Astellas*, AstraZeneca*, Merck Sharp & Dohme*, Mundipharma*, and Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma* Expert testimony: Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma* Grants / research support: Amgen*, Janssen-Cilag*, Otsuka*, and Roche* Speaker bureaus: Amgen*, Menarini*, Merck Sharp & Dohme*, Mundipharma, and Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma* Travel: Amgen* and Sanofi* *Monies paid to institution. Consultancy: Akebia, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, Relypsa, and Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma Methods Chair Wolfgang C. He assumed his current position as chief of nephrology at Baylor College of Medicine in September 2014. His main areas of research interest include comparative effectiveness and safety research of treatment strategies for anemia, as well as of various interventions for cardiovascular disease in patients with kidney disease. His clinical passion lies in providing quality kidney care to the predominantly disadvantaged and un(der)insured population in the public safety net health system of Harris County, Texas. Winkelmayer has authored over 300 peer-reviewed publications, and he has a particular interest in medical publishing. He currently serves as associate editor for the Journal of the American Medical Association, was a co-editor of the American Journal of Kidney Disease from 2007 to 2016, and has been appointed to several other editorial boards of leading nephrology and epidemiology journals. He has led the formation of state, national, and international networks to conduct high-quality, relevant trials in children.
Another study found abnormal defense-type autonomic reactions to novel stimuli among eight-monthold infants who had been exposed to epidurals at birth atrial fibrillation buy indapamide 1.5mg without prescription, compared with normal orienting reactions among unexposed infants hypertension food purchase indapamide overnight delivery. Long-term follow-up studies of monkey offspring exposed to epidurals also suggest developmental impacts. Given current widespread exposures, the full effects of epidurals on the baby in the short and longer term are critical areas for future research. Epidural Analgesia and Breastfeeding Epidurals may negatively impact breastfeeding success, with some evidence for shortened duration, but studies are contradictory, and high-quality research is lacking. Exposure to both epidurals and synthetic oxytocin in labor may significantly reduce maternal oxytocin release with breastfeeding. Many factors contribute to breastfeeding initiation and continuation, including maternal and fetal/newborn hormones and other factors. Given current widespread exposures, and the increasingly recognized detrimental effects in mother and baby of not breastfeeding, the full effects of epidurals on breastfeeding are critical areas for future research. Epidural Analgesia and Maternal Adaptations Epidural-related reductions in oxytocin, especially the oxytocin peak at birth, could potentially affect maternal adaptations in women, as has been demonstrated in animals. Studies in women have found subtle disturbances in maternal adaptations and in maternal-newborn interactions that may compromise evolving attachment. In the sheep studies, primiparous ewes, and those administered early epidurals were more affected than their multiparous and later-administration counterparts. Epidural-associated shifts in newborn neurobehavior and functioning may also contribute. Epidural impacts on memory and reward Epidural-related oxytocin disruptions, and the related co-interventions, may contribute to dissatisfaction with the experience of birth. Loss of positive oxytocin effects on memory may contribute to a stronger memory of labor pain and distress. Studies have shown that, while women using an epidural generally experience effective pain relief,614, 658 they are no more satisfied with the birth overall,658-662 and may even be more dissatisfied with their birth experience, compared with women who used no analgesia. In relation to oxytocin hormonal physiology, an in-labor non-emergency cesarean may be the most beneficial type of cesarean for mother and baby. In addition, following a cesarean, mother and baby may also miss postpartum skin-to-skin contact during the early sensitive period (see "Postpartum sensitive period" in 3. Non-hormonal aspects of surgery will obviously influence benefit/harm considerations. This may also indicate her risk of postpartum hemorrhage (see "Oxytocin and postpartum hemorrhage" in 3. Mother and baby will have experienced some labor processes and hormonal activation. Fewer uterine oxytocin receptors due to lack of prelabor physiologic preparations with prelabor cesarean, or to receptor desensitization following prolonged synthetic oxytocin exposure in labor, may increase risk of postpartum hemorrhage. The frequent lack of mothernewborn skin-to-skin contact after cesarean section could also contribute to increased hemorrhage risks. Levels of immature forms of the oxytocin molecule are elevated following cesarean, with unknown implications. Following in-labor unplanned cesarean, oxytocin and prolactin release may be reduced, possibly reflecting a prolonged delay to first breastfeed. Early mother-newborn contact and breastfeeding initiation may be important following cesarean to optimize hormonal physiology for both. Cesarean and Maternal Adaptations and Attachment Peaks of oxytocin and other hormones released during labor, birth, and the early postpartum period promote maternal adaptations that enhance infant care and survival. The absence of these peaks has major impacts on maternal behaviors in animals, but high-quality human research is lacking. Research has suggested poorer maternal adaptations, elevated risk of postpartum depression, and the possibility of post-traumatic stress disorder, along with a reduction in self-esteem from pregnancy levels. Researchers have also found a decrease in the expected shifts in maternal personality-decreased anxiety and increased "social desirability" (3. Given current high rates of cesarean section, and concerns about maternal postpartum psychological well-being, these are critical areas for future research.
Syndromes
- To do this, you will be be asked to cough deeply and spit the substance that comes up from the lungs (sputum) into a container.
- Blood chemistries, and liver function tests, such as CHEM-20
- Medical conditions that cause the liver to make too much bilirubin, such as chronic hemolytic anemia, including sickle cell anemia
- You get canker sores more than 2 or 3 times a year.
- Throat swelling (may also cause breathing difficulty)
- Constant hunger
- Oxygen
Comparative Data for Agents in Hypertensive Emergency (continued) Agents Compared Population Study Design Key Findings Labetalol vs blood pressure chart meaning buy generic indapamide 2.5mg online. Intravenous labetalol compared with intravenous nicardipine in the management of hypertension in critically ill patients hypertension first line buy indapamide 2.5mg fast delivery. A multicenter comparison of outcomes associated with intravenous nitroprusside and nicardipine treatment among patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Postoperative hypertension: a multicenter, prospective, randomized comparison between intravenous nicardipine and sodium nitroprusside. Nicardipine versus nitroprusside infusion as antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive emergencies. Nicardipine is superior to esmolol for the management of postcraniotomy emergence hypertension: a randomized open-label study. Comparison of intravenous nicardipine and nitroglycerin to control systemic hypertension after coronary artery bypass grafting. Clevidipine versus nicardipine for acute blood pressure reduction in a neuroscience intensive care population. Comparison of clevidipine with sodium nitroprusside in the control of blood pressure after coronary artery surgery. Cerebral hemodynamics during treatment with sodium nitroprusside versus labetalol in malignant hypertension. Retrospective evaluation of nicardipine versus labetalol for blood pressure control in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Severe hypertension in pregnancy: hydralazine or labetalol: a randomized clinical trial. Additional conclusions support the cautioned use of sodium nitroprusside for hypertensive emergencies presenting with neurologic injury. Furthermore, clevidipine may have a better blood pressure variability profile than nitroglycerin or sodium nitroprusside, lead to a lesser volume administered than nicardipine, and allow potentially faster attainment of blood pressure goals than the other agents. Again, however, despite these advantages, major clinical outcomes have not been affected. Guideline Recommendations and Consensus Opinions for Unique Presentations of Hypertensive Emergency Because robust studies supporting one agent over another regarding clinical outcomes are lacking, several medications can be used for the various presentations of hypertensive emergency. Understanding the safety profiles of each medication and data published in comparative studies (see Table 1-6) is important. Table 1-7 lists the individual agents, potential indications, and key considerations for use. Current available guidelines and consensus opinions support the data synthesized in Table 1-7. For acute ischemic stroke, the guidelines do not recommend a single specific agent or class of agents but state that an individualized approach is most appropriate, with consideration of agents such as labetalol, nicardipine, hydralazine, and enalaprilat (Jauch 2013). For patients with cocaine-induced hypertension, benzodiazepines are an effective first-line therapy, but additional blood pressure control may be warranted (Richards 2006). Relationship of blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy, and outcome in ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Lower treatment blood pressure is associated with greatest reduction in hematoma growth after acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Earlier blood pressure-lowering and greater attenuation of hematoma growth in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, for patients with hypertensive emergency caused by pheochromocytoma, phentolamine is largely considered the drug of choice (Prejbisz 2011). Concurrent loop diuretics should also be administered with considerations for renal replacement therapy, as needed, for volume removal (Rhoney 2009). In addition, the clinician must consider whether a patient qualifies as an exception to the general treatment principles of hypertensive emergency (compelling condition). Each patient will qualify for continuous monitoring to assess for achievement of target goal(s) and avoidance of overaggressive, unintentional correction. Furthermore, close monitoring is required to evaluate for adverse effects from the medications selected.
Generic indapamide 1.5 mg with mastercard. Nephron Function.