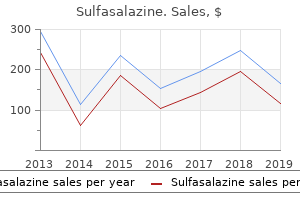
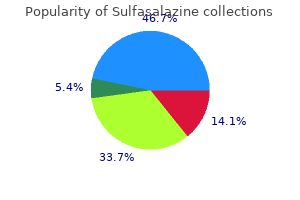
"Order sulfasalazine mastercard, pacific pain treatment center".
By: I. Tangach, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Program Director, Tufts University School of Medicine
Zinc is also known affect leukocyte functions such as phagocytosis and T-lymphocyte-mediated immune responses groin pain treatment video order sulfasalazine in united states online. Dietary supplementation or therapeutic treatment with vitamin A and zinc may be a cheap yet effective means of preventing or treating infections in highly susceptible populations knee pain treatment options buy sulfasalazine 500mg. Additional studies, however, are required to better define the types of pathogens and the specific human populations that may benefit from such therapy. Cell-mediated immunity is decreased as judged by reduced number and function of thymus-dependent lymphocytes, impaired delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions, and decreased production of lymphokines. Concentration of secretory IgA is reduced and there are fewer intraepithelial lymphocytes. Antibody responses following viral vaccine administration are reduced and there is decrease in natural killer cell activity. These changes are observed also in certain selected nutrient deficiencies, such as that of vitamin A. Impact of large-dose vitamin A supplementation on childhood diarrhoea, respiratory disease and growth. During the 12 month study period, there was a significant reduction in the incidence of diarrhoea (P < 0. Serum retinol and IgA levels of the treatment group were significantly higher than that of control group (P < 0. It was concluded that supplementation with large doses of vitamin A decreased the incidence and severity of diarrhoea and respiratory disease in these children, possibly through enhanced activity of the immune system, but had no effect on growth over 1 year. Vitamin A is required for regulation of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) expression by interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma in a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Vitamin A prevents the decline in immunoglobulin A and Th2 cytokine levels in small intestinal mucosa of protein-malnourished mice. However, in this paper we report that vitamin A-deficient Wistar rats had much reduced IgA+ plasma cells in the ileal lamina propria (eightfold reduction from 470 cells/mm(2), P = 0. In conclusion, the marked decrease of lamina propria IgA+ plasma cells may be one cause of the high diarrhoeal mortality in vitamin A deficiency. Effects of combination dietary conjugated linoleic acid with vitamin A (retinol) and selenium on the response of the immunoglobulin production in mice. Vitamin A for preventing secondary infections in children with measles-a systematic review. Measles severity and serum retinol (vitamin A) concentration among children in the United States. Plasma vitamin A levels in measles and malnourished pediatric patients and their implications in therapeutics. The mean retinol plasma levels return to within normal limits after 8 days of either routine treatment or vitamin A supplementation. Vitamin A supplementation enhances specific IgG antibody levels and total lymphocyte numbers while improving morbidity in measles. Vitamin A levels of children with measles have not been studied in developed countries. Children with low levels were more likely to have fever at a temperature of 40 degrees C or higher (68% vs 44%), to have fever for 7 days or more (54% vs 23%), and to be hospitalized (55% vs 30%). Our data show that many children younger than 2 years in New York City have low vitamin A levels when ill with measles, and that such children seem to have lower measles-specific antibody levels and increased morbidity. Clinicians may wish to consider vitamin A therapy for children younger than 2 years with severe measles. Children with autism had 9 species of Clostridium not found in controls, whereas controls yielded only 3 species not found in children with autism. In gastric and duodenal specimens, the most striking finding was total absence of non-spore-forming anaerobes and microaerophilic bacteria from control children and significant numbers of such bacteria from children with autism. These studies demonstrate significant alterations in the upper and lower intestinal flora of children with late-onset autism and may provide insights into the nature of this disorder. Over the past decade the incidence of both colonization and infection with other Candida species, particularly C parapsilosis, has risen dramatically. Microbial factors also augment colonization, including the ability of Candida to adhere to human epithelium. Role of nutrients and bacterial colonization in the development of intestinal host defense.
The most common method of fractionating cells is to use differential centrifugation: 1 treatment pain genital herpes buy cheap sulfasalazine 500 mg. This filtrate is now called a cell-free extract back pain treatment for dogs generic sulfasalazine 500 mg on line, and is capable of carrying out most of the normal cell reactions. Centrifuge supernatant at very high speed (300 000 x g for 3 h) this pellets ribososmes, which can be resuspended 8. The vast majority of living organisms are too small to be seen in any detail with the human eye, and cells and their organelles can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. The resolution of a microscope is ultimately limited by the wavelength of light used (400-600nm for visible light). To improve the resolution a shorter wavelength of light is needed, and sometimes microscopes have blue filters for this purpose (because blue has the shortest wavelength of visible light). Different Kinds of Microscope Light Microscopes these are the oldest, simplest and most widely-used form of microscopy. Specimens are illuminated with light, which is focused using glass lenses and viewed using the eye or photographic film. Specimens can be living or dead, but often need to be coloured with a coloured stain to make them visible. Transmission microscopes have a resolution of about 200nm, which is good enough to see tissues and cells, but not the details of cell organelles. The specimen is illumined with invisible ultraviolet radiation, and the stained objects emit visible light, so they can be seen even if the object is smaller than the wavelength of light. By combining scan of different layers in a computer, a three-dimensional image an be built up. Electron Microscopes this uses a beam of electrons, rather than electromagnetic radiation, to "illuminate" the specimen. This may seem strange, but electrons behave like waves and can easily be produced (using a hot wire), focused (using electromagnets) and detected (using a phosphor screen or photographic film). A beam of electrons has an effective wavelength of less than 1nm, so can be used to resolve small sub-cellular ultrastructure. This is the most common form of electron microscope and has the best resolution (<1nm). Using a Magnification Factor Sometimes the image has a magnification factor on it. Always M 1000 convert your answer to appropriate units, usually m for cells and organelles. The image size and bar length must be measured in the same units bar length (usually mm), and the actual size will come out in the same units as the bar scale. It controls how substances can move in and out of the cell and is responsible for many other properties of the cell as well. The membranes that surround the nucleus and other organelles are almost identical to the cell membrane. Membranes are composed of phospholipids, proteins and carbohydrates arranged as shown in this diagram. This hydrophobic layer acts as a barrier to most molecules, effectively isolating the two sides of the membrane. Different kinds of membranes can contain phospholipids with different fatty acids, affecting the strength and flexibility of the membrane, and animal cell membranes also contain cholesterol linking the fatty acids together and so stabilising and strengthening the membrane. The proteins usually span from one side of the phospholipid bilayer to the other (integral proteins), but can also sit on one of the surfaces (peripheral proteins). They can slide around the membrane very quickly and collide with each other, but can never flip from one side to the other. Most transport of small molecules across the membrane take place through integral proteins.
Discount sulfasalazine 500 mg on line. What is interventional pain treatment? - Bradley Reid MD | UCLA Pain Center.
The same geological period is also marked by the appearance of many modern groups of insects pain treatment algorithm cheapest generic sulfasalazine uk, including pollinating insects that played a key role in ecology and the evolution of flowering plants pain treatment for bladder infection buy discount sulfasalazine line. Although several hypotheses have been offered to explain this sudden profusion and variety of flowering plants, none have garnered the consensus of paleobotanists (scientists who study ancient plants). New data in comparative genomics and paleobotany have, however, shed some light on the evolution of angiosperms. Rather than being derived from gymnosperms, angiosperms form a sister clade (a species and its descendents) that developed in parallel with the gymnosperms. The two innovative structures of flowers and fruit represent an improved reproductive strategy that served to protect the embryo, while increasing genetic variability and range. Paleobotanists debate whether angiosperms evolved from small woody bushes, or were basal angiosperms related to tropical grasses. Both views draw support from cladistics studies, and the so-called woody magnoliid hypothesis-which proposes that the early ancestors of angiosperms were shrubs-also offers molecular biological evidence. A few other angiosperm groups called basal angiosperms, are viewed as primitive because they branched off early from the phylogenetic tree. Most modern angiosperms are classified as either monocots or eudicots, based on the structure of their leaves and embryos. Basal angiosperms, such as water lilies, are considered more primitive because they share morphological traits with both monocots and eudicots. Both fertilization and embryo development take place inside an anatomical structure that provides a stable system of sexual reproduction largely sheltered from environmental fluctuations. Flowering plants are the most diverse phylum on Earth after insects; flowers come in a bewildering array of sizes, shapes, colors, smells, and arrangements. Most flowers have a mutualistic pollinator, with the distinctive features of flowers reflecting the nature of the pollination agent. The relationship between pollinator and flower characteristics is one of the great examples of coevolution. The surrounding tissues of the ovary thicken, developing into a fruit that will protect the seed and often ensure its dispersal over a wide geographic range. Many attract animals that will eat the fruit and pass the seeds through their digestive systems, then deposit the seeds in another location. Cockleburs are covered with stiff, hooked spines that can hook into fur (or clothing) and hitch a ride on an animal for long distances. The cockleburs that clung to the velvet trousers of an enterprising Swiss hiker, George de Mestral, inspired his invention of the loop and hook fastener he named Velcro. Phylogeny is the science that describes the relative connections between organisms, in terms of ancestral and descendant species. Each branching point, called a node, is the point at which a single taxonomic group (taxon), such as a species, separates into two or more species. Traditional methods involve comparison of homologous anatomical structures and embryonic development, assuming that closely related organisms share anatomical features during embryo development. Some traits that disappear in the adult are present in the embryo; for example, a human fetus, at one point, has a tail. The study of fossil records shows the intermediate stages that link an ancestral form to its descendants. Most of these approaches are imprecise and lend themselves to multiple interpretations. As the tools of molecular biology and computational analysis have been developed and perfected in recent years, a new generation of tree-building methods has taken shape. Once the sequences of interest are obtained, they are compared with existing sequences in databases such as GenBank, which is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Sophisticated computer analysis programs determine the percentage of sequence identity or homology. In some cases, prior results from morphological studies have been confirmed: for example, confirming Amborella trichopoda as the most primitive angiosperm known. Paraphyletic groups are those in which not all members are descendants of a single common ancestor. Their characteristics include naked seeds, separate female and male gametes, pollination by wind, and tracheids (which transport water and solutes in the vascular system). Gymnosperm seeds are not enclosed in an ovary; rather, they are exposed on cones or modified leaves.
Over the past decade chronic pain syndrome treatment guidelines discount sulfasalazine 500mg line, a significant upswing in research has occurred to examine the biologic basis of autism sciatic nerve pain treatment exercises purchase sulfasalazine overnight delivery. Recent clinical studies have revealed a high prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms, inflammation, and dysfunction in children with autism. Mild to moderate degrees of inflammation were found in both the upper and lower intestinal tract. In addition, decreased sulfation capacity of the liver, pathologic intestinal permeability, increased secretory response to intravenous secretin injection, and decreased digestive enzyme activities were reported in many children with autism. Treatment of digestive problems appears to have positive effects on autistic behavior. These new observations represent only a piece of the unsolved autism "puzzle" and should stimulate more research into the brain-gut connection. Autistic disorder is a pervasive developmental disorder manifested in the first 3 years of life by dysfunction in social interaction and communication. Many efforts have been made to explore the biologic basis of this disorder, but the etiology remains unknown. Recent publications describing upper gastrointestinal abnormalities and ileocolitis have focused attention on gastrointestinal function and morphology in these children. High prevalence of histologic abnormalities in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and colon, and dysfunction of liver conjugation capacity and intestinal permeability were reported. Three surveys conducted in the United States described high prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autistic disorder. We report three children with autistic spectrum disorders who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and intravenous administration of secretin to stimulate pancreaticobiliary secretion. All three had an increased pancreaticobiliary secretory response when compared with nonautistic patients (7. These clinical observations suggest an association between gastrointestinal and brain function in patients with autistic behavior. Plasma from 11 normally developing adults (25 years 5 months to 55 years 5 months) was also tested. In conclusion, this study failed to replicate the findings of others and questions the validity of the opioid peptide excess theory for the cause of autism. This editorial briefly reviews the significance of lymphoid nodular hyperplasia in the intestinal tract of children with autistic spectrum disorder. The distinction between physiological and pathological lymphoid hyperplasia of the intestinal tract is of importance in the context of a possible causative link with autism. A primary intestinal lesion may occur as part of the broad spectrum of immunological disorders to which autistic children are prone. This could result in increased intestinal permeability to peptides of dietary origin which may then lead to disruption of neuroregulatory mechanisms required for normal brain development. Alternatively, there could be a primary defect in the translocation and processing of factors derived from the intestinal lumen. These possibilities deserve further investigation and should not be lost in the fog of the controversy regarding the role of measles/mumps/rubella vaccination in the aetiology of autistic spectrum disorder. It is not known whether the virus, if confirmed to be present in these patients, derives from either wild strains or vaccine strains. Positive samples were sequenced directly, in nucleotides 8393-8676 (H region) or 5325-5465 (from noncoding F to coding F region). In these syndromes urinary peptide abnormalities, derived from gluten, gliadin, and casein, are reported. The aim of this single blind study was to evaluate effect of gluten and casein-free diet for children with autistic syndromes and urinary peptide abnormalities. We could identify no report that describes the prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders in a representative group of children with a diagnosis of autism compared with appropriate controls. Thus, we found no evidence upon which to base a confident conclusion as to whether gastrointestinal symptoms are more common in children with than without autism.