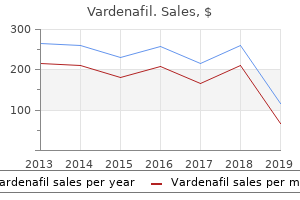
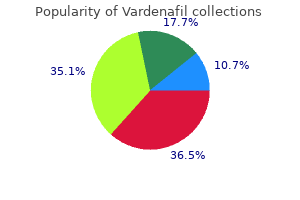
"Buy 10mg vardenafil visa, erectile dysfunction what doctor".
By: V. Cobryn, M.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, University of California, San Diego School of Medicine
Principles of Perceptual Development Recent evidence now addresses some of these important developmental questions erectile dysfunction questions to ask order 10 mg vardenafil mastercard. The Development of Perception 93 In a series of studies erectile dysfunction brochure best buy vardenafil, we found support for three basic principles of intersensory learning. First, global, amodal relations are detected developmentally prior to nested amodal relations (Bahrick, 2001). Nested amodal relations are more specific and are detectable within each synchronous impact. They convey more detail about the intersensory event such as its substance (rigidity vs. Bahrick (2001) habituated infants to naturalistic events depicting single and compound objects striking a surface, producing their natural impact sounds. Bahrick of this nested amodal information was significantly greater than detection of global synchrony. Early detection of temporal synchrony is important because temporal synchrony can specify the unity of the audiovisual event. Once infants attend to a unitary event, differentiation of further relations can then proceed in a veridical manner. However, attention to a sound and a sight that do not belong together would be maladaptive and would lead to learning of incongruent intersensory relations. A second developmental principle is that detection of amodal relations in a given domain developmentally precedes detection of arbitrary, modality-specific relations. Modality-specific information is information that is specified by only a single sense modality. For example, color and pattern are specific to vision, whereas pitch and timber are specific to audition. An intersensory relation between modality-specific information is typically arbitrary and must be learned. So is the relation between the pitch of an impact sound and the color of an object, or that between a speech sound and the appearance of the object it represents, or the relation between the visual appearance of a container and the temperature or taste of its contents. Bahrick (1992, 1994) found that by 3 months of age infants detected amodal temporal synchrony and temporal information specifying object composition in single and compound objects striking a surface. However, it was not until the age of 7 months that they detected the arbitrary, modality-specific relation between the pitch of the sounds and the colors and shapes of the moving objects, even though at 3 months of age infants could discriminate among all the objects and their sounds. Further, it was found that even when the modality-specific properties were made more highly discriminable, the amodal relations were nevertheless perceived developmentally prior to the arbitrary, modality-specific relations (Bahrick, 2000). There appears to be a developmental lag between the detection of amodal and modality-specific audiovisual relations provided by a given event. In contrast, if no common synchrony, rhythm, the Development of Perception 95 or tempo is detected, the association between the appearance of the face and sound of the voice is less likely to be learned. This principle was found to apply to intersensory learning about the arbitrary relation between the appearance of an object and the speech sound paired with it (Gogate & Bahrick, 1998), the color/pattern of an object and its tactually experienced shape (Hernandez-Reif & Bahrick, 2001), and the visual appearance of a single or compound object striking a surface and the particular sound it produced (Bahrick, 1988, 1992, 1994). Even newborns show evidence of learning arbitrary audiovisual relations in the presence of amodal information but not in its absence (Slater, Quinn, Brown, & Hayes, 1999). Studies of a variety of events perceived through various sensory modalities now suggest that detection of amodal information such as temporal synchrony can promote further differentiation of the unitary event and lead to learning about nested properties and, finally, about arbitrary, modality-specific relations. This developmental sequence where learning progresses in order of increasing specificity (from detection of amodal to arbitrary, modality-specific relations) is adaptive because it can promote learning about consistencies and regularities across the senses that are context-independent prior to learning about more context-dependent relations (see Bahrick, 2001). Early detection of amodal relations fosters appropriate, veridical generalizations and minimizes inappropriate generalizations about relations that vary across contexts and are specific to certain events. In this manner, detection of amodal relations can guide and constrain learning about modality-specific relations such that general principles. This progression from global to specific is adaptive and provides a means of organizing, guiding, and constraining perceptual learning in a way that will efficiently lead to the intermodal knowledge of adult perceivers. The above research has revealed important principles of perceptual development explaining attentional allocation, perception, and learning about events experienced multimodally. Bahrick where infants received simultaneous audible and visible stimulation, as is typical in the natural environment. However, stimulation from a given event does not always reach multiple sense modalities.
Erectile dysfunction warrants a thorough evaluation so the physician or other healthcare provider can look for all possible causes erectile dysfunction drugs after prostate surgery vardenafil 10 mg overnight delivery, especially diabetes (which can cause autonomic neuropathy) and other disorders listed above erectile dysfunction etiology order vardenafil from india. A complete physical examination should be conducted by the general physician and urologist. Many people report spontaneous and unexplained drenching sweat, often awakening them from sleep and creating a need to change bedclothes. Botulinum toxin A can be effective in small injections for hyperhidrosis of the palms and armpits. For some people, being in the "off" state can increase a sensation of pain, and adjusting medication dosage and intervals will lead to improvement. Camptocormia is an example of dystonia characterized by severe bending at the waist, causing back pain or spasm. Depending on the timing of dystonic pain, several different approaches may prove helpful. Early morning dystonia often improves with movement and/or the first dose of dopaminergic medication. In some cases, the severity of morning dystonia merits a subcutaneous injection of apomorphine. If dystonia occurs as a wearing-off phenomenon, minimizing the "off" period with dopaminergic therapy is the goal of treatment. Radicular, or nerve root, pain should be evaluated for a compressed root or nerve lesion. Akathitic discomfort is an inner restlessness that makes it difficult for one to sit still and is different from dyskinesias or anxiety. These symptoms should be addressed by the physician to rule out other primary causes of abdominal and chest pain. Some options include conventional antiinflammatories, muscle relaxants, gabapentin, tricyclic antidepressants and additional dopaminergic doses. Opiates should be used only in severe cases, and referral to a pain specialist is recommended. Several non-pharmacologic techniques include regular exercise, heating pads, ice packs and massage. It also may be related to other medical conditions such as arthritis or neuropathy. The higher brain structures are where you think, and the deep structures are where those thoughts are translated into actions, particularly movement. In addition to improving symptoms, scientists are increasingly convinced that exercise may slow disease progression. Establishing early exercise habits is an essential part of overall disease management. Executive function can be impaired by problems with working memory (measured by how many things you can keep track of simultaneously), problems with keeping focused on a task and responding to changes. The parts of the brain that perform executive function tasks are the same ones that help you to apply motor learning in changing environments. For example, you use these executive function centers when you go from walking inside the house to walking outside. You also use your executive function centers when you think about how to improve a motor skill how to do a task you know how to do better or faster. In the past, when scientists studied how exercise affected the brain they always studied basic aerobic training such as biking or walking on a treadmill, track or around the community. When you exercise aerobically, you make your heart healthier and you improve how your body uses oxygen. Studies of aerobic exercise have shown that it can help improve age-related changes in executive function. They are studying what is the right "dose" of exercise to get the best benefits, including looking at how to balance the benefits of exercise versus the risk that exercising too much might increase your risk of falls or injury.
Purchase 20 mg vardenafil amex. How to Have Stronger Erections.
In this paradigm infants were shown target acts on objects but not allowed to touch or handle the objects at Time-1 impotence biking cheap vardenafil online amex. After the delay erectile dysfunction herbal treatment discount vardenafil 20mg with mastercard, the objects were presented to the infants, and deferred imitation was assessed. Thus, infants could not be repeating their own actions with the objects, because interaction with them had been barred at Time-1. Using this design, deferred imitation of actions on objects has now been documented in infants as young as 6 to 9 months of age (Barr, Dowden, & Hayne, 1996; Heimann & Meltzoff, 1996; Meltzoff, 1988b). Even if deferred imitation is possible, there are other hurdles to overcome before the theoretical implications are clear. For example, if deferred imitation in the pre18-month-olds was restricted to highly familiar behaviors, it would sharply limit the implications for representation. Meltzoff (1988a) showed infants an adult who leaned forward and pressed a panel with 150 Andrew N. The infants were not allowed to play with the panel and were sent home for a 1-week delay interval. The baseline rate of producing this novel act was 0 percent for the control groups who did not see the adult display. Researchers have investigated the length of delay that can be tolerated by young infants, with surprising results. Infants as young as 6 to 9 months of age successfully imitate after delays of 24 hours (Barr et al. Once formed, representations evidently tend to persist and can be used as the basis of subsequent action. In light of the evidence so far presented, there might be a temptation to tinker slightly with the classic theory to allow deferred imitation and representation at about 6 to 12 months old instead of 18 months. However, these capacities seem to be part of the initial state, at least when simple body actions are presented. Such facial imitation is representationally mediated: it has been demonstrated using an observation-only design, with novel gestures, and over long delays. Thus we infer that neonates have some primitive form of representation that allows them to organize action based on stimuli no longer in the perceptual field. Infants sucked on a pacifier while an adult demonstrated mouth opening and tongue protrusion (Meltzoff & Moore, 1977). This technique blocked infants from imitating while the display was in the perceptual field. The adult then stopped the demonstration, assumed a neutral face, and only then removed the pacifier. The results showed that 3-week-old infants imitated the gestures in the subsequent response period, despite the fact that the target gesture was no longer visible. Other studies have also reported early facial imitation when the gesture was no longer visible (Fontaine, 1984; Heimann, Nelson, & Schaller, 1989; Heimann & Schaller, 1985; Legerstee, 1991; Meltzoff & Moore, 1989). Theories of People and Things 151 Young infants have also been shown to imitate across longer delays. In one study, four groups of 6-week-old infants saw different gestures on Day 1 and returned on Day 2 to see the adult with a neutral pose (Meltzoff & Moore, 1994). The results showed that 6-week-old infants differentially imitated the gestures they saw 24 hours earlier. Finally, 6-week-old infants are able to imitate a somewhat novel gesture, a tongue-protrusion-to-the-side (Meltzoff & Moore, 1994, 1997). It is interesting that such young infants do not imitate this novel act on first try but modify their behavior over successive efforts, without feedback from the adult. Larger implications these findings impact theories of representational development (Hayne, 2002; Slater, 2002). Three inferences can be drawn: (1) representations can be formed from observation alone, without concomitant motor action; (2) representations are durable mental entities in the preverbal period; and (3) they are a sufficient basis on which to organize action.
Folic acid intervention also seemed to have improved red cell morphology in the study in Nigerian pregnant women by folic acid intervention (34) erectile dysfunction treatment high blood pressure vardenafil 10 mg on line. A preparation containing 15 micronutrients was compared to the same with added iron from around 13 weeks gestation in pregnant women in Mexico erectile dysfunction fast treatment buy discount vardenafil line. It is considered that premature and low birth weight infants are at considerable increased risk if 124 J. Several poorly designed interventions have not added any great conclusions in this area, as summarized by Fishman et al. They found a marked decline in low birth weight by a combination of iron-folic acid, which was not improved by adding other micronutrients. Also, folic acid alone had no effect, so the authors attribute the benefits to iron. Two intervention trials have been conducted in non-pregnant women using improvement in Hb response as an indication of response. Mackey and Picciano (40) conducted a small trial on 21 women on multivitamins, compared to the same multivitamin plus 1. The women seemed to have normal hemoglobin status to begin with, in that they were not anaemic or folate deficient. This study, though small, would seem to indicate some added benefit for folic acid. However, no obvious benefit was found in a large study of 624 non-pregnant Thai or Malaysian women (41). Mahomed (42) reviewed eight trials involving 5,449 women, and concluded that such supplements "had no detectable effect on any sustained measures of either maternal or fetal outcome. Again, there was no measurable effect on pregnancy outcome but again, there was an improvement in hemoglobin levels. The above studies in developing countries correspond to earlier experience in developed countries. Megaloblastic anemia in pregnancy, while recognized in earlier studies, became less and less obvious as diet and social conditions improved (3, 35). However, most studies would indicate that women who enter pregnancy with good stores have sufficient folate to show no signs or symptoms of megaloblastic anemia before delivery (3, 7). It is less clear why vitamin B12 deficiency leads to obvious cognitive or neurological sequale which seem to be absent in folate deficiency. Another obvious difference between the two vitamins is their prevalence, and reasons why they become deficient. Folate in its natural form is unstable, has significantly reduced bioavailability and is not abundant in almost any diet even in affluent countries. The evidence of a widespread prevalence of reduced status, even in those on excellent diets is ascribed to the presence of hypochlorhydria in significant proportions of all populations. This is due to gastric atrophy, with the absence of acid preventing the liberation of vitamin B12 from the bound form that it is present in foods. While it is less well documented, one could anticipate equally high prevalence of such malabsorption in developing coun- Nutritional anemia: B-vitamins 125 tries. It is simply a fact that the enzymes necessary to assemble this very large vitamin are only present in bacteria and some algae. Its synthesis is completely absent in plant and vegetables of all kinds, being only present in such foods by way of bacterial contamination. Vitamin B12 enters the human food chain exclusively through animal products, either as meat or animal products such as milk or milk products or eggs. Some strict vegans do consume products which would contain some of the vitamins via bacteria or algal synthesis. Thus, in general, vegetarians or more particularly, vegan communities are a high-risk group of being vitamin B12 deficient. This topic has recently been the subject of an extensive review by Stabler and Allen (45). They draw the distinction between those at risk from insufficient dietary intake and those who have impaired malabsorption. In the latter instance, there are two sub-categories, those with true pernicious anemia and subjects at risk of vitamin B12 malabsorption, because of gastric atrophy.