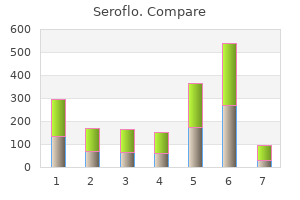
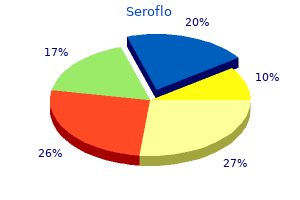
"Purchase seroflo amex, allergy forecast cincinnati".
By: Y. Vatras, MD
Associate Professor, Burrell College of Osteopathic Medicine at New Mexico State University
The symbols represent residual heterozygosity at any given generation allergy forecast hanover pa generic 250mcg seroflo mastercard, expressed as the percent of the original heterozygosity in the N1 generation allergy testing hot springs ar cheap seroflo uk. It takes only 10 generations to create an inbred congenic, while it takes 20 generations to create a standard inbred strain. This is because in creating a congenic, one of the parents is always 100% homozygous for the recipient genotype. By the 10th generation of backcrossing, the congenic strain is homozygous (recipient type) for 99. For inbreeding by sibling mating, it takes 30 generations of inbreeding to reach that percentage of homozygosity. Traditionally, however, congenics were created for a known monogenic trait by selecting for the desired phenotype at every generation. This approach is sometimes used today, especially when a genetic marker is unavailable. Selection based on phenotypes requires multiple strategies, based on the characteristics of the mutation. These strategies are described in Appendix H, "Transfer of a Mutant or Variant Allele to a New Genetic Background by Phenotypic Selection. At the Jackson Laboratory, we A drawback with creating congenics using recommend placing markers about every 10 cM. This can be a major Speed congenic technology can reduce the impediment to progress of a research program. In number of required backcrosses from 10 to 5 contrast, creating a speed congenic takes just and save 1-1/2 years. Although the process to create a another benefit: any residual heterozygosity is speed congenic is more expensive, the time well-defined. For information on the speed congenic service at A conplastic strain has the nuclear genome of the Jackson Laboratory, visit one strain and the mitochondrial genome of Conplastic strains are used mostly to us at 1-800-422-6423 (North America) or 1-207study the role of mitochondrial genes in energy 288-6294 (International). The effects of backcrossing on homozygosity and residual heterozygosity of conplastic strains is the same as for congenics (Figure 3. Considerations In a congenic strain, a short chromosomal segment-containing multiple genes rather than a single gene-is transferred to an inbred strain by successive backcrossing. Along with the allele of interest, this segment includes donor-type alleles that are commonly referred to as "passenger genes" or "linked genes. Thus, a variant phenotype observed in a new congenic strain cannot be attributed exclusively to an interaction of the target gene with the recipient genotype. The Jackson Laboratory Handbook on Genetically Standardized Mice Chapter 3: Categories of Laboratory Mice-Definitions, Uses, Nomenclature 57 3. Maintenance breeding strategies Following the creation of an inbred congenic strain or segregating inbred congenic strain, maintenance of congenic strains is the same as for single locus mutations (see 3. Controls For congenic mice, the selection of controls is based on the nature of the mutation. Nomenclature Nomenclature for congenic strains includes information about recipient and donor strains as well as the locus of interest. Nomenclature for conplastic strains includes names of the mitochondrial donor strain and the recipient strain. Numbers of generations of backcrossing and inbreeding (designated by N for backcross generation and F for filial generation) generally are not reflected in the name, but are important pieces of information that should be provided by the supplier. For details about the number of backcross generations for a particular strain, check with the supplier. Research examples Use of congenic strains in discovery of function of Lith1 and Lith2 genes. Congenic strains were instrumental in the discovery of Lith1 and Lith2 genes, both of which determine cholesterol gallstone formation (Paigen et al. They fed these mice a lithogenic diet and mapped the phenotype "gallstone formation.
There are no clearly identifiable predisposing factors for most adverse skin reactions allergy treatment in homeopathy order 250mcg seroflo amex. Probably not immunological in origin allergy medicine okay to take while pregnant purchase seroflo with a mastercard, the reaction may be related to prostaglandin inhibition in a patient whose cutaneous mastocytes are more susceptible to the stabilizing effect of prostaglandins. Skin testing in patients with a history of urticarial and/or anaphylactic reactions to analgesics is of little value in identifying patients at risk and can be dangerous (208,209). Skin pigmentation and environmental factors that influence the radiant exposure dose are clearly very important in determining the risk of a phototoxic reaction. Since the extreme rarity of life-threatening reactions, such as erythema multiforme and toxic epidermal necrolysis, suggests individual susceptibility, efforts have been made to identify subjects at risk. A 28-year-old man had been using a bendazac-containing ointment for his atopic dermatitis for 6 months, together with topical corticosteroids. Pseudoporphyria Pseudoporphyria is a photodistributed bullous disorder with clinical and histological features similar to those of porphyria cutanea tarda, but without accompanying abnormalities of porphyrin metabolism. Pseudoporphyria associated with naproxen (15 mg/kg/day) has been reported in a child (233). Inhibition of glycosaminoglycan synthesis in joint cartilage, inhibition of necrotic bone repair by reduced synthesis of vasodilator prostaglandins, which have been shown both in vitro and in animals, and deprivation of protective painful stimuli are possible mechanisms. The first prospective study showed that hip osteoarthritis progressed more rapidly in patients taking indometacin, a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, than in those taking azapropazone, a weak inhibitor (234). This suggests that one should be cautious with long-term use of the more potent cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors in patients whose joints are severely compromised by osteoarthritis. The second study showed that the risk of progression of knee osteoarthritis increased in patients treated with indometacin for 1 year (235). A study on a small group of patients treated with piroxicam for osteoarthritis of the knee supported the hypothesis that deprivation of painful stimuli lets the patient put more load on the joint, increasing the risk of more rapid progression of the disease (237). A 14-year-old boy had contact allergy to indometacin gel used for a sprained ankle (222). Patch tests with the indometacin gel and pure indometacin 1% in petrolatum were positive. A case of photoallergy from local piketoprofen has been reported (223), as have two cases of prolonged photosensitivity after contact photoallergy from ketoprofen, persisting for more than a year after withdrawal (224,225). A 65-year-old Caucasian woman developed a localized skin eruption within hours of using ketoprofen gel on her knees to relieve arthralgia (226). The lesions were pruritic, well-demarcated, and erythematous, and later became studded with vesicles and small bullae. A case of photoallergic contact dermatitis from aceclofenac has been reported (228). Photocontact dermatitis has been reported after topical application of dexketoprofen (Enangel), with positive photopatch tests to dexketoprofen 1% and piketoprofen 2% (229). Photopatch tests with Tantum verde as is and in 10% aqueous solution were positive: D1+, D2+, D3++. Photosensitization potentials and cross-reactivities of ketoprofen, suprofen, tiaprofenic acid, and benzophenone have been studied in guinea pigs (231). More recently a report of resensitization to bee stings associated with diclofenac has been received by the Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring in New Zealand. The patient, who had been successfully desensitized to bee venom many years before, developed life-threatening anaphylaxis after a bee sting while taking diclofenac (250). Furthermore they can impair the host defence mechanism against infection and can modulate the acute inflammatory response in such a way as to alter the course of infection, predisposing the patient to bacteremia, shock, and multiorgan failure (252,253). To be included in the analysis documentation of invasive streptococcal infection and necrotizing fasciitis was required. Finally, reports of these reactions include different, often imprecise, terms, making interpretation difficult. However, the figures are distorted, because some of these drugs are much more widely used than others.
Buy generic seroflo line. Untreated allergic reactions caused by food can be fatal.
Blood pressure is controlled in pari by the mechanisms that regulate cardiac output and peripheral resistance allergy shots cost no insurance discount seroflo 250mcg mastercard. Cardiac: output depends 011 the volume of blood discharged from the ventricle with each beat (stroke volume) and 011 the heart rate allergy symptoms lip swelling order 250mcg seroflo with visa. Changes in the diameter of arterioles, controlled by the vasomotor center of the medulla oblongata, regulate peripheral resistance. Venous blood flow is not a direct result of heart action; it depends on skeletal muscle contraction, breathing movements, and venoconstriction. T h e blood vessels form a closed circuit of tubes that transport blood between the heart and body cells. T h e arteries are adapted to carry relatively high pressure blood away from the heart. T h e wails of arteries and arterioles consist of layers of endothelium, smooth muscle, and connective tissue. Autonomic fibers that can stimulate vasoconstriction or vasodilation innervate smooth muscles in vessel walls. T h e capillary wall is a single layer of cells that forms a semipermeable membrane. Capillary permeability (1) Openings in the capillary walls are thin slits between endothelial cells. CapiI lary arrangement Capillary density varies directly with tissue metabolic rates. Regulation of capillary blood flow (l) Precapillary sphincters regulate capillary blood flow. T h e median cubital vein in die bend of the elbow is often used as a site for venipuncture, Tributaries of the brachiocephalic and azygos veins drain the abdominal and thoracic walls. T h e blood from the abdominal viscera generally enters the hepatic portal system and is carried to the liver. T h e liver helps regulate the blood concentrations of glucose, amino acids, and lipids. T h e deep veins include the tibial veins, and the superficial veins include the saphenous veins. T h e pulmonary circuit consists of vessels that carry blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, alveolar capillaries, and vessels that lead back to the left atrium. Tightly joined epithelial cells o f alveoli walls prevent most substances from entering the alveoli. Osmotic pressure rapidly draws water out of alveoli into the interstitial fluid, so alveoli do not fill with fluid. T h e systemic circuit is composed of vessels that lead from the heart to all body parts (including vessels supplying the heart itself) and back lo the heart. It includes the aorta and its branches as well as the system o f veins that return blood to the right atrium. T h e branches of the ascending aorta include the right and left coronary arteries. T h e branches of the aortic arch include the brachiocephalic, left common carotid, and left subclavian arteries. T h e abdominal aorta terminates by dividing into right and left common iliac arteries. Arteries to die neck, head, and brain include branches of the subclavian and common carotid arteries, Arteries to the shoulder and upper limb a. T h e subclavian artery passes into the arm, and in various regions, it is called the axillary and brachial artery. Arteries to the pelvis and lower limb the common iliac artery supplies the pelvic organs, gluteal region, and lower limb. Some degree of cholesterol deposition in blood vessels may be a normal part of aging, but accumulation may be great enough to lead to overt disease. Fibrous connective tissue and adipose tissue enlarge the heart by filling in when the number and size of cardiac muscle cells fall. Blood pressure increases with age, w h i l e resting heart rate decreases with age. R I T I C A L T H I N K I N G q ^ I f S T I O N S Given die way capillary blood flow is regulated, do y o u think it is wiser to rest or to exercise following a heavy meal? If a patient develops a blood clot in the femoral vein of the left lower limb and a portion of the clot breaks loose, where is the blood f l o w likely to carry the embolus?
Hence allergy medicine and pregnant 250 mcg seroflo with visa, light impulses pass through most layers of the retina before they reach the rods and cones allergy medicine no drowsiness seroflo 250 mcg without prescription. The anterior fifth of the inner layer, the pars ceca retinae, remains one cell layer thick. It later divides into the pars iridica retinae, which forms the inner layer of the iris, and the pars ciliaris retinae, which participates in formation of the ciliary body. Meanwhile, the region between the optic cup and the overlying surface epithelium is filled with loose mesenchyme. In the adult, the iris is formed by the pigment-containing external layer, the unpigmented internal layer of the optic cup, and a layer of richly vascularized connective tissue that contains the pupillary muscles. Externally, it is covered by a layer of mesenchyme that forms the ciliary muscle; on the inside, it is connected to the lens by a network of elastic fibers, the suspensory ligament or zonula. Contraction of the ciliary muscle changes tension in the ligament and controls curvature of the lens. Pigment layer of retina Sinus venosus sclerae Neural layer of retina Ciliary process Sphincter pupillae Ciliary muscles Anterior lens epithelium Dilator pupillae Sphincter pupillae Ciliary process Outer pigmented layer of iris Inner unpigmented layer of iris A B Figure 20. The rim of the optic cup is covered by mesenchyme, in which the sphincter and dilator pupillae develop from the underlying ectoderm. Chapter 20 Eye 333 Suspensory ligament Conjunctival sac Sclera Pigment layer Neural layer of the retina Anterior chamber Iridopupillary membrane Cornea Choroid Vitreous body Hyaloid artery Dura Ectoderm Eyelid Posterior chamber Iris Ciliary body Outer vascular layer Inner vascular layer Optic nerve Figure 20. By the end of the seventh week, these primary lens fibers reach the anterior wall of the lens vesicle. Growth of the lens is not finished at this stage, however, since new (secondary) lens fibers are continuously added to the central core. This tissue soon differentiates into an inner layer comparable with the pia mater of the brain and an outer layer comparable with the dura mater. The inner layer later forms a highly vascularized pigmented layer known as the choroid; the outer layer develops into the sclera and is continuous with the dura mater around the optic nerve. Differentiation of mesenchymal layers overlying the anterior aspect of the eye is different. The anterior chamber forms through vacuolization and splits the mesenchyme into an inner layer in front of the lens and iris, the iridopupillary membrane, and an outer layer continuous with the sclera, the substantia propria of the cornea. Hence, the cornea is formed by (1) an epithelial layer derived from the surface ectoderm, (2) the substantia propria or stroma, which is continuous with the sclera, and (3) an epithelial layer, which borders the anterior chamber. The posterior chamber is the space between the iris anteriorly and the lens and ciliary body posteriorly. The anterior and posterior chambers communicate with each other through the pupil and are filled with fluid called the aqueous humor produced by the ciliary process of the ciliary body. The clear aqueous humor circulates from the posterior chamber into the anterior chamber providing nutrients for the avascular cornea and lens. From the anterior chamber, the fluid passes through the scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm) at the iridocorneal angle where it is resorbed into the bloodstream. Here, it forms the hyaloid vessels, which during intrauterine life supply the lens and form the vascular layer on the inner surface of the retina. The interstitial spaces of this network later fill with a transparent gelatinous substance, forming the vitreous body. The hyaloid vessels in this region are obliterated and disappear during fetal life, leaving behind the hyaloid canal. The nerve fibers of the retina returning to the brain lie among cells of the inner wall of the stalk. During the seventh week, the choroid fissure closes, and a narrow tunnel forms inside the optic stalk. As a result of the continuously increasing number of nerve fibers, the inner wall of the stalk grows, and the inside and outside walls of the stalk fuse. Cells of the inner layer provide a network of neuroglia that support the optic nerve fibers.