"Order ondansetron 8 mg without a prescription, medicine man".
By: W. Charles, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, TCU and UNTHSC School of Medicine
Political ecology is rooted here in its proximity to the processes of ecological degradation and environmental conflict medications resembling percocet 512 purchase ondansetron 4mg line, existentially connected with its history symptoms zyrtec overdose discount ondansetron 4mg fast delivery, its cultures and its landscapes. While Anglophone political ecology takes socio-environmental transformation of the Third World as critical themes and privileged objects of study, political ecology of the South is inserted in its processes of emancipation. If the former expresses itself discursively in its aim to deconstruct the dominant social rationality and to undertake case studies regarding the impacts of power on socio-environmental relations, the political ecology of the Third World is constructed as a discursive amalgam of academic and political actors, as a dialogue of knowledges between theoretical thought, participatory research and the social imaginaries of the people, in alliance with resistance movements and their political strategies for emancipation and reappropriation of their biocultural legacy (Guha 1989; Guha and Gagdil 1992; Arnold and Guha 1995; Shiva 1988; Escobar et al. The political ecology of the Third World does not limit its purpose to the analysis of the processes of socioenvironmental conflicts, or to the sociology of resistance movements. It has a theoretical and historical commitment to the construction of a sustainable future and of other possible worlds. In this sense, political ecology ceases to be just a new discipline or epistemic, interdisciplinary field. It understands the transition toward sustainability as a process of deconstructing the rationality of modernity and constructing in its place an environmental rationality in the confluence of cultural diversity and environmental complexity. Political ecology is the field where a dialogue of knowledges plays out understood as the encountering of cultural beings constituted by their knowledge the confrontation and alliances of diverse modes of being-in-the-world; in the re-encounter of nature and culture 70 the power-full distribution of knowledge (Leff 2001, 2004). The political ecology of the South is constructed through a dense discursive network of theoretical frameworks, social imaginaries and lifeworlds. It is the encounter between ontologies and rationalities, between modes of being-in-the-world and modes of appropriation of nature. It is the reinvention of identities and the movements of rexistence7 of people with nature. In this perspective, the field of political ecology is moving toward the inquiry and practice of political ontology (Blaser 2009; Escobar 2013; Leff 2014a: chapter 3). In the irruption of environmental complexity diverse epistemic communities have emerged, drawing from different theoretical sources and disciplinary identities that converge in the field of political ecology. Beyond comprising a new inter-scientific discipline, political ecology is forged as the field of forces where the dialectics of socio-environmental conflicts is expressed in a diversity of geographic, cultural and political contexts. However, the different modes of intelligibility and approaches to socio-environmental processes are not generated simply as a reflection in theory of different geographical and cultural conditions. The intellectual and academic environment has played an important role in constructing different analytical perspectives and theoretical developments in regional approaches to political ecology. Thus, in Latin America, the research of Eric Wolf and Angel Palerm (1972) regarding the ecological potential of agricultural systems in Mesoamerica, the analysis of John Murra (1956) regarding the organization of geographical space and vertical ecological zones8 of the original people of Tawantiunsuyu, the Geography of Hunger of Josuй de Castro (1975) and the studies of the indigenato of Darcy Ribeiro (1973), opened new avenues of anthropological, ethnographic, geographical and agrarian analysis tied to the knowledges and practices of traditional cultures in the territories of the South. The theories of dependency and internal colonialism (Gonzбlez Casanova 1965; Stavenhagen 1965), ecological liberation theory (Boff 1996), of decolonization and of the ethics of liberation (Dussel 1998; Quijano 2000; Lander 2000; Mignolo 2000, 2011; Mignolo and Escobar 2009), and the theories of agro-ecological practices, are inscribed in the call for a knowledge from/of the South (Sousa Santos 2008), and the emergence of a Latin American environmental thought (Leff 2012), that from the perspective of an ecology of difference and territorial conflict, puts its stamp on the political ecology of Latin America (Leff 2003, 2014a, 2014b). Regional political ecologies are more a mosaic and a map of the diversity of foci regarding the relations of power that are exercised in different socio-ecological contexts and processes, from the forms of analysis, the tactics of negotiation and the strategies for resolving environmental conflicts. The field of political ecology is the meeting place of rationalities, logics of meaning and political practices in which a will to power is manifest in diverse and frequently opposing strategies in the struggle over life territories. It is the space of collision and resistance of the territorializing processes of hegemonic geopolitics of sustainable development (Leff 2002) that invade and foreclose possible alternative strategies for constructing sustainable worlds. In the field of political ecology socio-environmental movements unfold to resist the degradation of their livelihoods, reinventing collective identities and designing alternative strategies to reappropriate the biocultural heritage of the peoples of the Earth in order to construct a sustainable future. Political ecology of the North and the winds from the South Political ecology emerges from, and is manifested within, the rural problematic, the agrarian question and rural studies. It is within this space that environmental problems are radicalized as territorial conflicts, where disputes over modes and rights to appropriation of nature are played out. Surely today these processes are expanding to the oceans, the atmosphere and the cities. Leff it is in rural areas where these conflicts are the sharpest, and where possibilities open for constructing new, negentropic ways of (re)producing life. If, during the twentieth century, the countryside was the scene of agrarian revolutions and the struggle over land, the rural sphere is today the space where the processes of reappropriation and reconstruction of territory unfold. Beyond the struggles for land and the management of agrarian systems of the division of lands as an economic development policy for agrarian subsistence and traditional ways of life political ecology is the field in which the struggles over deterritorialization and re-territorialization are deployed.
Their viscoelasticity provides a mechanical barrier between tissues and allows the surgeon more space for manipulation with less trauma to surrounding tissues medicine pill identification buy ondansetron overnight, particularly the corneal endothelium treatment diabetes order ondansetron without prescription. In posterior segment surgery, it is used to separate tissue away from the retina and as a tamponade to maneuver tissue, such as a detached retina, back into place for reattachment. Sodium hyaluronate is a high molecular weight polysaccharide which is widely distributed throughout the tissues of the body of animals and humans. The viscoelastic materials used as ocular surgical aids are specic fractions from animal tissue, which are highly puried to remove foreign proteins and are tested to be nonantigenic and noninЇammatory in the eye. The puried fraction is formulated to yield a high viscoelasticity determined by the interplay of molecular weight and concentration. The solution is packaged in disposable glass syringes, which are terminally sterilized and aseptically packaged so that they can be used in the sterile surgical eld (Healon1, ProVisc1, Amvisc1). However, the ophthalmologist uses available parenteral dosage forms to deliver antiinfectives, corticosterioids, and anesthetic products to achieve higher therapeutic concentrations intraocularly than can ordinarily be achieved by topical or systemic administration. However, these drugs are usually administered by subconjunctival or retrobulbar injection and rarely are they injected directly in the eye [301]. The approved intraocular miotics, carbachol (Miostat1) and acetylcholine (Miochol1), are injected into the anterior chamber at the end of cataract surgery to constrict the pupil and allow the iris to cover the implanted intraocular lens. Nonpyrogenic solutions of sterile hydroxypropyl methylcellulose are also used as ocular surgical aids similar to the viscoelastics in cataract surgery (OcuCoat1). Since it is not a natural product, it does not have the antigenic potential of the other viscoelastics. It can be stored at room temperature, whereas the sodium hyaluronate solutions must be stored in the refrigerator. The frequency of injection, based on the clinical progression of the disease, is every 2±4 weeks. Contact lenses used medically for the treatment of certain corneal diseases are called bandage lenses. Evolution of Contact Lenses In 1508 Leonardo da Vinci conceived the concept of the contact lens. Although they were safe and eective, these lenses were uniformly uncomfortable, thus suppressing their potential use for contact lens wear. Since then, signicant technological advances have been made in lens materials, lens fabrication, and lens designs [303]. Consequently, a phenomenal growth in lens wearers necessitated the need for, and development of, lens care products. They are treated with systemic administration, but with the need for higher localized ocular therapeutic concentrations, products have been developed and approved for direct administration into the vitreous cavity. The sterile implant is a tablet of ganciclovir with magnesium stearate and is coated to retard drug release with polyvinyl alcohol and ethylene vinyl acetate polymers such that the device when surgically implanted in the vitreous cavity releases drug over a 5to 8-month period. When the implant is visually observed to be depleted, and based on clinical observation of the progression of the disease, it is surgically removed and replaced with a new implant. The implant is provided in a sterile Tyvek package and contains a suture tab for handling prior to and during implantation so that the polymer release rate controlling coating is not damaged. Also, precautions for handling and disposal of antineoplastic agents should be observed. It is formulated as a sterile and preservative-free solution and supplied in single-use vials (Vitravene1). The product is administered directly into the vitreous cavity posterior to the limbus through a 30-gauge needle. Cross-linkers, such as ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate, and initiators such as benzyl peroxide in appropriate amounts are added for polymerization and to achieve desirable physical and chemical properties. Table 5 gives a list of monomers, comonomers, and crosslinkers along with their eects on polymer properties. Adequate levels of oxygen are necessary to maintain normal corneal metabolism [306]. Lenses that are poorly designed and worn overnight deprive the cornea of oxygen, causing edema [307]. Generally, oxygen permeability for soft lenses is acceptable when worn on a daily basis. Hypoxia related side eects such as corneal swelling, epithelial microcysts, limbal redness, neovascularization, epithelial polymegathism and blebs are well known and mainly observed with extended contact lens wear. Recent development of hydrophilic silicone hydrogel materials combines the high oxygen permeability of silicone with the good water and ion permeability of hydrogels resulting in acceptable extended wear lenses.
Ondansetron 8 mg on-line. 131006 SHINee Jonghyun 샤이니 종현 - 상사병(Symptoms) @ SHINee COMEBACK SPECIAL in GANGNAM HANRYU FESTIVAL.
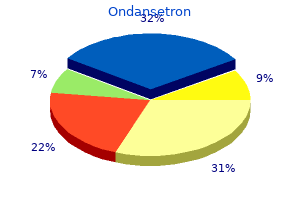
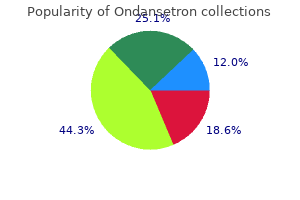
Heracleum montanum (Masterwort). Ondansetron.
- Dosing considerations for Masterwort.
- What is Masterwort?
- How does Masterwort work?
- Muscle cramps, stomach disorders, digestion problems, diarrhea, inflammation of the stomach and intestines, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96561
The principal formulation strategy is to stabilize the protein using clinically acceptable additives (excipients) or through the use of suitable pharmaceutical-processing technologies medicine used for anxiety generic 8mg ondansetron fast delivery. From an ease of use and processing perspective treatment uterine cancer order 4 mg ondansetron free shipping, a solution formulation is preferred and is typically the primary goal in developing a parenteral formulation. However, many proteins are very unstable in solution and may not give acceptable shelf life as solution formulations even when refrigerated at 2±8 C. In such cases, freeze-drying or lyophilization is often employed to inhibit the degradative processes that often occur in solutions. Table 2 lists examples of formulations for some of the currently approved biopharmaceuticals. The principles used in developing these types of products are described in the following sections. Protein Stabilization in Solution Using Additives Proteins are generally most stable in solutions that mimic their natural environment. For example, mature insulin precipitates under conditions of pH and salt concentration at which serum proteins are soluble [97]. The stability of b-galactosidase is greatly enhanced in the presence of milk proteins [98]. Many proteins like caseins that bind to Ca2 generally require small amounts of the ion to maintain their native structure during purication [99,100]. The protein formulation program may begin with an assessment of the eect of pH, ionic strength, and oxygen on the stability and solubility of the protein. Buer salt selection for the formulation is guided by the pH range of interest and the acceptability of the buer for use in a medicinal product. The eect of dierent salts and their concentrations on protein stability was also reviewed in Sec. In addition to aecting protein stability, salt concentration may have a profound eect on protein solubility and aggregation. Schein [101] provides a useful overview of the means of stabilizing proteins against aggregation and of methods to determine, predict, and increase solubility. Perlman and Nguyen [102] report that, for human growth hormone, a sodium phosphate buer concentration of about 5 mM produced less aggregation of the protein, as measured by light scattering, compared with solutions of 2. These authors further highlight the formulation development of tissue plasminogen activator. For this agent, the solubility of the protein at the optimally stable pH was insucient for the therapeutic application. A positively charged amino acid, arginine, was included in the formulation to increase the solubility of the protein at the desired pH range. Antioxidants such as methionine and sodium thiosulfate were added to the formulation to reduce the oxidation. Although ionic surfactants are often associated with denaturation of proteins [104], the nonionic surfactant polysorbate 80 has been included in several marketed formulations and serves to inhibit protein aggregation. The mechanism may be the greater tendency of the surfactant molecules to align themselves at the liquid/ air interface, excluding the protein from the interface and inhibiting surface denaturation. Solution additives that are known to stabilize the native proteins in solution may inhibit aggregation and enhance solubility. A diverse range of chemical additives are known to stabilize proteins in solution. Timashe and colleagues have provided an extensive examination of the eects of solvent additives on protein stability [105]. The unifying mechanism for protein stabilization by these cosolvents is related to their preferential exclusion from the protein surface. With the cosolvent preferentially excluded, the protein surface is Copyright © 2002 Marcel Dekker, Inc. The unfolded state as well as the oligomeric and aggregated states of proteins become thermodynamically less favorable than the native state. In the rst class, interactions are determined by the properties of the solvent; in the second class, interaction depends on the chemical nature of the protein surface. In the rst class of cosolvents, steric exclusion of the larger additive molecule, compared with the smaller water molecule, can account for the preferential hydration, as occurs with polyethylene glycol. Also in the rst class of cosolvents, additives such as sugars, amino acids, and many salts may act by increasing the surface tension of water, which leads to preferential hydration at the protein solvent interface. Here, the contact with the water-cosolvent mixture is thermodynamically less favorable than the protein-water contact, forcing the cosolvent away from the surface into the bulk solvent.
Starches remain a popular glidant medicine 029 generic ondansetron 4mg mastercard, in particular those with the larger grain sizes such as potato starch medicine zyprexa generic ondansetron 8mg otc, possibly because of their additional value as a disintegrant in the formulation. Concentrations up to 10% are common, but it should be appreciated that excess may result in exactly the opposite eect of that desired. Talc is also widely used and has the advantage that it is superior to starches in minimizing any tendency for material to stick Copyright © 2002 Marcel Dekker, Inc. Because of its totally insoluble nature, and hence potential retardant eect of dissolution, concentration must be strictly limited and should rarely exceed 5%. In fact, the best overall compromise may be realized by using a mixture of starch and talc. Among those quoted in the literature are pyrogenic silica in concentrations as low as 0. The former has the additional property of being able to scavenge moisture, which might otherwise contribute to restricted Їow characteristics. Phyllosilicates, in addition to talc and silica, have recently been evaluated for their use as tableting excipients. Although they show some promise, current levels of metallic impurities are currently too high for use in pharmaceutical preparations. Although not a frictional eect, this results in material preferentially sticking to the punch faces and gives rise to tablets with rough surfaces. This eect, called picking, can also arise in formulations containing excess moisture. Normally, the lubricants present in the tableting mass also act as antiadherents, but in the worst cases it may be necessary to add more starch or even talc to overcome the defect. So by judicious choice of a combination of excipients, all of these undesirable effects of the tableting process can be minimized. Materials used to modify dissolution can be incorporated in the formulation on either a dry or wet basis. Absorbents Some tablet formulations call for the inclusion of a small amount of semisolid, or even semiliquid, ingredient. It is highly desirable that any such component should be adsorbed onto, or absorbed into, one of the powders. In cases where none of the other excipients in the formulation is able to act as a carrier, an absorbent may have to be included. When oily substances, such as volatile-favoring agents, are involved, magnesium oxide and magnesium carbonate have been found to be suitable for this purpose. An absorbent may also be necessary when the formulation contains a hygroscopic ingredient, especially when absorption of moisture produces a cohesive powder that will not feed properly to the tablet press. One special problem in the tableting of volatile medicaments, like nitroglycerin, is the loss of activity Copyright © 2002 Marcel Dekker, Inc. Alternatively, cross-linked povidone can also be used to enhance the stability of this particular drug. When an oil Їavoring is prone to oxidation, it may be protected by a special type of encapsulation involving spray drying or an aqueous emulsion containing the Їavor. The emulgent used in spray-dried products may be starch or acacia gum giving rise to the so-called dry Їavors. Flavoring Agents Making a formulation palatable enough to be chewed may result in enhanced availability of the drug. Sweetening agents such as dextrose, mannitol, saccharin, and sucrose are widely used as Їavoring agents (see Table 12). When choosing a Їavoring agent, however, one must carefully assess potential incompatibilities that may exist between the agent and the active ingredient. Perhaps the most extensively documented examples concern nitroglycerin tablets, which at one time were formulated in a chocolate base containing nonalkalized cocoa. Flavoring agents proper are commonly volatile oils that have been dissolved in alcohol and sprayed onto the dried granules or have simply been adsorbed onto another excipient. They are added immediately prior to compression to avoid loss through volatilization. Their main role is to facilitate identication and to enhance the esthetic appearance of the product.