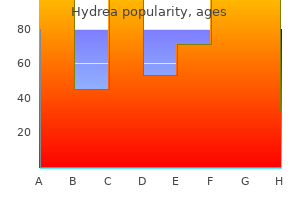
"Discount hydrea on line, medicine daughter lyrics".
By: P. Tangach, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of California, Irvine School of Medicine
If meningococcal infection is suspected treatment viral meningitis cheap hydrea 500 mg on line, or the child is extremely ill and meningitis is suspected treatment zenker diverticulum order generic hydrea line, start treatment prior to investigation. Pneumococcus and HiB can continue to spike temperatures for 710 days: consider imaging of the head for effusion/empyema or local abscess formation. If given, they should: · Ideally be administered before the first antibiotic dose at a dose of 0. Contacts For HiB and meningococcus, with rifampicin at 10 mg/kg for 4 or 2 days, respectively. Fluid restriction may further compromise cerebral circulation, so before restricting fluids check plasma and urinary sodium and osmolality, and urine output. Pathogenesis · Primary infection occurs when the tubercle bacillus is inhaled into the lungs and taken up by alveolar macrophages. In the majority of cases, this primary infection passes unnoticed, with only the development of a positive tuberculin skin test to indicate that infection has taken place. Diagnosis is often difficult to confirm initially, and needs to be based on clinical suspicion. Acetazolamide or ventriculoperitoneal shunting may be used for hydrocephalus (usually communicating). Mortality Mortality is 1050% depending on stage of presentation; 30% have residual neurological sequelae. Clinical features include headache, fever and neck stiffness following a prodromal flu-like illness. Causative agents Enteroviruses (responsible for 85% of cases) Include echovirus, Coxsackie, poliovirus. All cause diffuse rashes with or without more specific features: · Echovirus: conjunctivitis, myopathy. Mumps Parotitis, orchitis, pancreatitis with elevated amylase and lipase (extraneural manifestations occur in 50% cases). Features are of developmental stagnation, and later neurological and general cognitive regression with pyramidal signs, hypokinesis and evolving dysphagia and feeding difficulties. In older children, deteriorating school performance, social withdrawal, and emotional lability are seen. May have insidious onset with abnormal behaviour/memory problems that can be mistaken for psychiatric illness. The former is usually found in the immunocompetent and typically leads to arterial stroke (see b p. Small vessel encephalitis usually occurs in the immunosuppressed: zoster infection occurred weeks to months earlier, followed by chronic progressive encephalitis. In neonates there are widespread signal abnormality- hypointense on T1, and hyperintense on T2. If relapse occurs, re-treat and consider prophylaxis with oral aciclovir or valaciclovir for 90 days. Non-viral causes of infectious encephalitis Viral causes are found in approximately 50% cases of encephalitis. Consider the following if no viral cause is found especially if there is an appropriate travel history or if the child is immunocompromised. Other causes of pyogenic meningitis/abscess: especially if septicaemia and micro-abscesses are possible. Rickettsial (rash usually present) · Rickettsia rickettsii Rocky Mountain spotted fever). Anterior horn cell infection Polio Polio virus is an enterovirus causing biphasic febrile illness with initial prodrome then further fever with acute-onset asymmetrical progressive flaccid paralysis of one or more limbs. Children may develop later onset of weakness >30 yrs after initial illness-post-polio syndrome. Enterovirus 71 Causes outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease in the Asia-Pacific region. May develop polio-like neurological manifestations with or without meningitis or encephalitis. Anaerobes such as bacteroides, Streptococcus milleri and Fusobacterium are also commonly found.
Transesophageal echocardiography treatment 4 burns order hydrea 500 mg online, therefore treatment vaginitis generic hydrea 500mg with visa, requires that the patient be sedated or undergo general anesthesia. Transthoracic Echocardiography can be used to determine Preload and Stroke Volume/Cardiac Output. Preload can be evaluated in two ways: By estimating the left ventricle end diastolic volume and by evaluating the inferior vena cava diameter. Stroke volume/cardiac output can also be evaluated in two ways: By using the Simpson Method and by measure how much blood flows through the left ventricle outflow tract during each heart beat. The Simpson Method involves tracing the endocardial border of the left ventricle at end systole (top left) and at end diastole (top right). The calculated end systolic volume is then subtracted from the end diastolic volume to determine the stroke volume. The cardiac output can then be estimated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate. Note that echocardiography provides twodimensional images of a three dimensional structure. On the right side, an Mmode beam is shown being directed across the inferior vena cava as it enters the right atrium. To evaluate left ventricle preload, the diameter of the inferior vena cava is measured at inspiration and at expiration. The objective is to assess whether respiratory variation in the inferior vena cava diameter is present. On the right, its diameter is measured after zooming in on the structure during mid-systole. Using the diameter measurement, a Cross Sectional Area of the left ventricle outflow tract can be calculated. This is part of the calculation to determine how much blood is flowing through the left ventricle outflow tract with each heart beat. The other part of the calculation involves determination of the Velocity Time Integral using the apical five chamber view. Increasing "preload" (1) will improve ventricular output in normal, hyperdynamic, and failing hearts within certain limits. Venodilators (4) and diuretics (5) can decrease ventricular volume by causing "pooling" of blood outside the central venous system and by reducing intravascular volume, respectively. The apical five chamber view can be used to calculate the Velocity Time Integral using pulse doppler imaging. On the left, the pulse doppler beam is directed in the line of the left ventricular outflow tract. On the right, a pulse doppler measurement is taken just proximal to the aortic valve and the Velocity Time Integral is calculated by determining the area under the curve. The left ventricle stroke volume can be calculated by multiplying the Cross Sectional Area of the left ventricle outflow tract and the Velocity Time Integral. The details of the measurements described in this figure legend are beyond the scope of this course. However, the idea that left ventricle preload and stroke volume/cardiac output can be easily determined using echocardiography should be appreciated. Clinically, it is useful to plot "preload" versus ventricular output (the Starling relationship). By doing so, one can easily identify normal, hypodynamic, and hyperdynamic ventricular function. The inotropic state of the cardiac muscle as well as the "afterload" determines the Starling Curve on which the heart "moves. Thompson reports that during the past month she developed an intolerance to lying flat and now requires four pillows to prop her head up when sleeping. She also describes fatigue that has worsened over the course of the past six weeks. She had been breastfeeding, but her fatigue and shortness of breath have forced her to transition the baby to formula feeds.
Though medicine 524 buy generic hydrea 500 mg on line, asymptomatic medicine 7 year program purchase hydrea 500 mg amex, if untreated, secondary syphilis can relapse (latent syphilis) and more episodes of relapses may show a more granulomatous histology in skin lesions and progress to the next stage. They occur in most organs but in skin, subcutaneous tissue, bone, Joints and testis. In the liver, scarring as a result of gummas may cause a distinctive hepatic lesion known as hepar lobatum. The lesions include aortitis, aortic value regurgitation, aortic aneurysm, and coronary artery ostia stenosis. The proximal aorta affected shows a tree -barking appearance as a result of medial scarring and secondary atherosclerosis. Endartereritis and periaortitis of the vasa vasoum in the wall of the aorta, is responsible for aortic lesions and in time, this may dilate and form aneurysm and eventually rupture classically in the arch. Treponemas do not invade the placental tissue or the fetus until the fifth month of gestation (since immunologic competence only commences then) syphilis causes late abortion, still birth or death soon after delivery or It may persist in latent forms to become apparent only during childhood or adult life. In primary and secondary stages, the fetus is heavily infected and may die of hydrops in utero or shortly after birth. After maternal second stage, the effects of congenital syphilis are progressively less severe. Children infected in utero who are sero -positive show no lesions until two or more years after birth are classified as having late congenital syphilis. Malaria Malaria is caused by the intracellular protozoan parasite called Plasmodium species and plasomodium Faliprium is the worldwide infections that affect 100 million people and kill 1 to 1. Falciparum): Infected humans produce gametocytes that mosquitoes acquire on feeding. Repeated cycles of parasitemia occur with subsequent ruptures of these cells with resultant clinical manifestations such as chills, fever etc. Individuals with sickle cell trait are resistant to malaria because the red cells that are parasitized in these individuals are removed by the spleen. Morphology: Spleen enlarged upto 1000gm (normally 150grams) and this splenomegaly can be attributed to increased phagocytosis in splenic reticuloendothelial cells in chronic malaria. Liver kuffer cells are heavily laden with malarial pigments, parasites, and cellular debris. Pigmented phagocytes may be dispersed through out bone marrow, lymph nodes, subcutaneous tissues and lungs. These patients manifest diffuse symmetric encephalopathy; brain vessels are plugged with parasitized red cells. Hypoglycemia- result from failure of hepatic gluconeogenesis & glucose consumption by the host and the parasite lactic acidosis -due to anaerobic glycolysis, non cardiogenic pulmonary edema, renal impairment, anemias etc 178 P. In other types of malaria only subpopulations of erythrocytes are parasitized, and thus low level parasitemias and more modest anemias occur. Malaria in pregnancy In pregnancy, malaria may be associated with hypoglycemia, fetal distress syndrome and low birth weight. Malaria in children Most of the estimated 1-3 million persons who die of falciparum malaria each year are young African children. Convulsion, coma, hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis and severe anemia are relatively common. Transfusion malaria Malaria can be transmitted by blood transfusion, needle -stick injury, sharing of needles by infected drug addicts, or organ transplants. The incubation period is short because there is no pre-erythrocytic stage of development. Leishmaniasis Definition: Chronic inflammatory disease of skin, mucous membranes or viscera caused by obligate intracellular Kinetoplastid protozoal parasites (Leishmania species) transmitted through infected sand fly. Different leishmanial parasites in new and old world appeared to show tropism related to temperature, because parasites that cause visceral disease grow at 37% in vitro whereas parasite that cause multiple diseases grow only at 340c. Leishmania are phagocytozed by macrophage and acidity within phagolysosome induces them to transform into amastigate from promatigate by losing flagella. In contrast, down regulation of the immune response that lead to anergy and progressive diseases may be caused by and iC3b. Cutaneous leishmaniasis Localized single ulcer on exposed skin (slowly expanding and irregular borders, usually heals within 6 months by involution. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis Lesions of diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis resembles lepromatous leprosy nodules. The lesions do not ulcerate but contain vast aggregates of foamy macrophages filled with leishmania.
Purchase hydrea overnight. Are you depressed? (TEST).
In order to receive honors for the clerkship as a whole medicine mountain scout ranch order hydrea paypal, a student has to receive honors from the faculty and meet the honors criteria set for the mini-board exam (50th% or higher for the Pediatric Clerkship) medications with aspirin cheap hydrea online visa. If a student is felt to be in jeopardy of not successfully completing the clinical (subjective) portion of the clerkship, the Clerkship Director will meet with the particular student involved to develop a plan of action designed specifically to address the deficiency noted. Failure of the National mini-board exam will result in a grade of incomplete (I) for the entire clerkship. If the exam is failed the second time, the student will be required to retake the entire clerkship. Information included here should include: · Onset of symptom · How symptom developed (including setting) · Location of symptom · Quality of symptom · Quantity of symptom · Timing of symptom (duration, frequency) · Setting in which symptoms occurs (time of day) · Aggravating factors 16 Alleviating factors What has been done for symptom (therapies, medications, previous doctor visits for symptom) · Associated symptoms · Pertinent negative symptoms · Exposures to illness Example of a history of present illness: · "This is the 1st hospital admission for this 4 year old black male who was well until 5 days prior to admission when the patient developed bruising. Over the last 2 days although some of the bruises have faded, new ones have appeared and the patient has developed a red rash. The parents have sought no medical attention for this until this time and gave no medications to the child. The parents deny that the patient has had vomiting, diarrhea, fever, swollen glands, or appeared pale. The child was noted to have had an ear infection about 2 weeks prior to the onset of this problem. The infant cried immediately after delivery and went home with the mother 3 days after birth. Neonatal History · Any problems after birth, length of initial stay in hospital, any problems at home. Feeding History Infant · Breastfed or formula fed, frequency of feedings, type and volume of formula, supplements to feeding, difficulty with feeds Child · Food likes and dislikes, amount and type of food eaten Family history Can draw out family tree or just list illnesses and affected family members. Be sure to list relative affected and whether diseases are on paternal or maternal side. Social History Ask adolescents about sexual activity, smoking, alcohol and drug use. Determine who lives in home, type of house, city or well water, sewer system or septic tank, are the parents employed outside the home, who cares for the child while parents are working, smokers, pets, etc. Review of Systems (meant to be a brief catalog of head-to-toe symptoms; do not have to ask every symptom on every patient. Talk quietly and in a friendly manner and tell older children what you are about to do. Remove clothes gradually to prevent chilling and to allow the older child to maintain some degree of modesty. Begin the exam with the area that is least likely to be uncomfortable for the child. Oxygen saturation · State whether this value is while the patient is breathing room air or if receiving oxygen, state how much. Weight, height, and head circumference (if under 2) · Plot these on standard growth charts and record percentiles. If the infant is Rh+, the mother will be given Rhogam to prevent Rh isoimmunization with future pregnancies. Labor and Delivery Notes o these should be read looking for the following information: Medications given to mom · In particular, antibiotics, narcotics, and magnesium sulfate. The Barlow test detects the unstable hip dislocating from the acetabulum and with a positive Barlow test, a palpable "clunk" is felt as the femoral head exits the acetabulum posteriorly. The Ortolani test elicits the sensation of the already dislocated hip reducing and with a positive Ortolani test, a "clunk" is felt as the dislocated femoral head reduces into the acetabulum. The fingers then push the greater trochanter of the femur anteriorly and medially to return the femoral head to the acetabulum. Forms which describe the 12 components of the exam and contain the scoring chart can be found in the well baby nursery. List as the 1st assessment, the primary diagnosis that led to the visit or hospitalization and the assessment that will be the focus of your formulation.