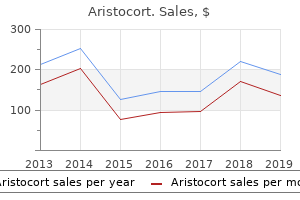
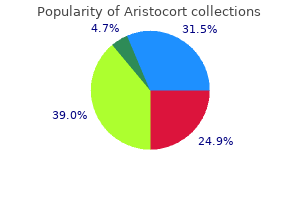
"Buy aristocort 4mg on-line, allergy symptoms loss of voice".
By: B. Treslott, M.S., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences College of Osteopathic Medicine
Basal insulin is usually prescribed in conjunction with metformin and sometimes one additional noninsulin agent wheat allergy symptoms joint pain purchase aristocort 4mg without prescription. There have been substantial increases in the price of insulin over the past decade and the cost-effectiveness of different antihyperglycemic agents is an important consideration when selecting therapies (36) allergy forecast kansas city purchase aristocort 4mg line. A follow-on U-100 (100 units/mL) glargine product (basaglar) is now available in the U. If A1C is,8% (64 mmol/mol) when starting mealtime bolus insulin, consideration should be given to decreasing the basal insulin dose. Premixed Insulin Premixed insulin products contain both a basal and prandial component, allowing coverage of both basal and prandial needs with a single injection. Concentrated Insulin Products Many individuals with type 2 diabetes may require mealtime bolus insulin dosing in addition to basal insulin. Rapid-acting analogs are preferred due to their prompt onset of action after dosing. U-500 regular insulin, by definition, is five times as concentrated as U-100 regular insulin and has a delayed onset and longer duration of Table 8. U-300 glargine and U-200 degludec are three and two times as concentrated as their U-100 formulations, have longer durations of action, and allow higher doses of basal insulin administration per volume used. These concentrated preparations may be more comfortable for the patient and may improve adherence for patients with insulin resistance who require large doses of insulin. Inhaled Insulin Inhaled insulin is available for prandial use with a more limited dosing range. It is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and is not recommended in patients who smoke or who recently stopped smoking. When initiating combination injectable therapy, metformin therapy should be maintained while other oral agents may be discontinued on an individual basis to avoid unnecessarily complex or costly regimens. Once an insulin regimen is initiated, dose titration is important with adjustments made in both mealtime and basal insulins based on the blood glucose levels and an understanding of the pharmacodynamic profile of each formulation (pattern control). For example, providers may wish to consider regimen flexibility when devising a plan for the initiation and adjustment of insulin therapy in people with type 2 diabetes, with rapid-acting insulin offering greater flexibility in terms of meal planning than premixed insulin. If a patient is still above the A1C target on premixed insulin twice daily, consider switching to premixed analog insulin three times daily (70/30 aspart mix, 75/25 or 50/50 lispro mix). In general, three times daily premixed analog insulins have been found to be noninferior to basal-bolus regimens with similar rates of hypoglycemia (41). If a patient is still above the A1C target on basal insulin 1 single injection of rapidacting insulin before the largest meal, advance to a basal-bolus regimen with $2 injections of rapid-acting insulin before meals. Optimized mealtime insulin dosing for fat and protein in type 1 diabetes: application of a model-based approach to derive insulin doses for open-loop diabetes management. Impact of fat, protein, and glycemic index on postprandial glucose control in type 1 diabetes: implications for intensive diabetes management in the continuous glucose monitoring era. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Most youth with type 1 diabetes in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry do not meet American Diabetes Association or International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes clinical guidelines. Kmietowicz Z Insulin pumps improve control and reduce complications in children with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977986 S74 Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment Diabetes Care Volume 40, Supplement 1, January 2017 12. Outpatient insulin therapy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: scientific review. Inhaled technosphere insulin compared with injected prandial insulin in type 1 diabetes: a randomized 24-week trial. Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Comparative effectiveness and safety of medications for type 2 diabetes: an update including new drugs and 2-drug combinations. Metformincontaining Drugs: Drug Safety Communication Revised Warnings for Certain Patients With Reduced Kidney Function [Internet]. Safety, effectiveness, and cost of long-acting versus intermediate-acting insulin for type 1 diabetes: protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis with use of the Coccidioides antigen enzyme immunoassay allergy shots reactions swelling purchase aristocort 4mg on line. Role of Coccidioides Antigen Testing in the Cerebrospinal Fluid for the Diagnosis of Coccidioidal Meningitis allergy symptoms penicillin discount aristocort online mastercard. Comparison of oral fluconazole and itraconazole for progressive, nonmeningeal coccidioidomycosis. Fluconazole in the treatment of chronic pulmonary and nonmeningeal disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Other immune defects include quantitative and qualitative B-cell abnormalities that result in impaired pathogenspecific antibody production, abnormalities in neutrophil function or numbers, and abnormalities in alveolar macrophage function. Other risk factors for infection include the use of corticosteroids, severe malnutrition, hospitalization within the past 90 days, residence in a health care facility or nursing home, and chronic hemodialysis. Tachypnea and decreased arterial oxygen saturation indicate moderate-to-severe pneumonia, and in such cases, clinicians should strongly consider hospitalizing the patient. Patients with bacterial pneumonia typically have signs of focal consolidation, such as egophony, and/ or pleural effusion on lung examination. Individuals with bacterial pneumonia characteristically exhibit unilateral, focal, segmental, or lobar consolidation on chest radiograph. The frequency of these typical radiographic findings, however, may depend on the underlying bacterial pathogen. Noninvasive measurement of arterial oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry is an appropriate screening test. Arterial blood gas analysis is indicated for patients with evidence of hypoxemia suggested by noninvasive assessment and for patients who have tachypnea and/or respiratory distress. This includes greater long-term mortality, as hospitalization for pneumonia has been associated with increased mortality up to one year later. If previous radiographs are available, they should be reviewed to assess for new findings. The clinical diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia requires a demonstrable infiltrate by chest radiograph or other imaging technique in conjunction with compatible clinical symptoms and signs. Microbial identification can allow clinicians to target the specific pathogen(s) and discontinue broad spectrum antibiotic therapy and/or empiric therapy that targets non-bacterial pathogens. Bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage should be considered, especially if the differential diagnosis includes opportunistic pathogens such as Pneumocystis jirovecii. Specimens should ideally be obtained before initiation of antibiotics, or within 12 hours to 18 hours of such initiation. Microbiologic diagnostic testing is indicated whenever epidemiologic, clinical, or radiologic clues prompt suspicion of specific pathogens that could alter standard empirical management decisions. In general, Gram stain and culture of expectorated sputum should be performed only if a good-quality specimen can be obtained prior to (or not more than 1218 hours after) initiation of antibiotics, and quality performance measures for collection, transport, and processing of samples can be met. For intubated patients, an endotracheal aspirate sample should be obtained promptly after intubation, or bronchoscopy may be indicated. Diagnostic thoracentesis should be performed in all patients with pleural effusion if concern exists for accompanying empyema, and pleural fluid should be sent for microbiologic studies. Therapeutic thoracentesis should be performed to relieve respiratory distress secondary to a moderate-to-large-sized pleural effusion. Data demonstrate that smoking cessation can decrease the risk of bacterial pneumonia. However, antibiotic therapy should be administered promptly, without waiting for the results of diagnostic testing. Assessing Severity of Disease and Treatment Location Whether patients should be treated on an outpatient basis or admitted to the hospital depends on several factors. In addition to considerations regarding ability to take oral medications, adherence, and other confounding factors. Low risk patients for whom there are no other concerns regarding adherence or complicating factors can be treated as outpatients. Preferred beta-lactams are high-dose amoxicillin or amoxicillin-clavulanate; alternatives are cefpodoxime or cefuroxime. An oral respiratory fluoroquinolone (moxifloxacin or levofloxacin) should be used as an alternative to a beta lactam in patients who are allergic to penicillin.
Purchase aristocort with visa. Mayo Clinic Minute: Allergy or irritant? The truth about your rash.
C E D A C E D B D C 89 Family Medicine Modular Systems General Principles allergy symptoms for babies cheap 4 mg aristocort with visa, Including Normal Age-Related Findings and Care of the Well Patient Immune System Blood & Lymphoreticular System Behavioral Health Nervous System & Special Senses Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue Musculoskeletal System (% increases with the addition of the Musculoskeletal module) Cardiovascular System Respiratory System Gastrointestinal System Renal & Urinary System Pregnancy allergy shots alcohol aristocort 4mg on-line, Childbirth, & the Puerperium Female Reproductive System & Breast Male Reproductive System Endocrine System Multisystem Processes & Disorders Biostatistics, Epidemiology/Population Health, & Interpretation of the Medical Lit. Social Sciences Communication and interpersonal skills Medical ethics and jurisprudence Systems-based practice and patient safety Physician Task Health Maintenance, Prevention & Surveillance Diagnosis, including Foundational Science Concepts Pharmacotherapy, Intervention & Management Site of Care Ambulatory Patient Age Birth to 17 18 to 65 66 and older 5%10% 1%5% 1%5% 5%10% 1%5% 3%7% 5%10% 5%10% 5%10% 5%10% 1%5% 1%5% 1%5% 1%5% 5%10% 1%5% 1%5% 5%10% 20%25% 40%50% 25%30% 100% 15%20% 55%65% 15%20% 90 1. A 22-year-old college student comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of palpitations. She is a single mother and notes that her boyfriend has not helped with their infant daughter as much as he had promised. A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of pain and swelling of the right foot for 24 hours. One month ago, he was diagnosed with hypertension and started treatment with hydrochlorothiazide. Examination shows tenderness, swelling, erythema, and warmth of the right first metatarsophalangeal joint; range of motion is decreased. X-rays of the right foot show mild joint space narrowing and periarticular bony erosions of the metatarsophalangeal joint. A 23-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of painful urination and a clear urethral discharge. One month ago, he had similar symptoms and completed a course of doxycycline therapy for a chlamydial infection. He has been sexually active with one female partner for 2 years, and she takes an oral contraceptive. There is a grade 2/6, systolic, vibratory ejection murmur heard best at the fourth intercostal space in the left midclavicular line. D E D D A 94 Medicine Systems General Principles, Including Normal Age-Related Findings and Care of the Well Patient Immune System Blood & Lymphoreticular System Nervous System & Special Senses Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue Musculoskeletal System Cardiovascular System Respiratory System Gastrointestinal System Renal & Urinary System Female Reproductive System & Breast Male Reproductive System Endocrine System Multisystem Processes & Disorders Biostatistics, Epidemiology/Population Health, & Interpretation of the Medical Lit. Social Sciences, Including Medical Ethics and Jurisprudence Physician Task Applying Foundational Science Concepts Diagnosis: Knowledge Pertaining to History, Exam, Diagnostic Studies, & Patient Outcomes Health Maintenance, Pharmacotherapy, Intervention & Management Site of Care Ambulatory Emergency Department Inpatient Patient Age 17 to 65 66 and older 1%5% 1%5% 5%10% 5%10% 5%10% 5%10% 10%15% 10%15% 8%12% 8%12% 1%5% 1%5% 5%10% 3%7% 1%5% 1%5% 10%15% 50%55% 30%35% 55%65% 20%25% 15%20% 70%80% 20%30% 95 1. A 22-year-old woman with a 10-year history of asthma comes to the physician because she has had to increase her use of her albuterol inhaler during the past 6 weeks. She has a 2-year history of generalized anxiety disorder controlled with fluoxetine and a 5-year history of migraines. The migraines were well controlled with sumatriptan until 4 months ago when she began to have headaches twice weekly; propranolol was added to her regimen at that time. She says she has been under increased stress at graduate school and in her personal life during the past 3 months; during this period, she has been drinking an average of four cups of coffee daily (compared with her usual one cup daily). A 28-year-old woman has palpitations that occur approximately once a week, last 1-5 minutes, and consist of rapid, regular heart pounding. The episodes start and stop suddenly and have not been associated with chest discomfort or dyspnea. There is a midsystolic click at the apex and a grade 2/6, early systolic murmur at the upper left sternal border. A study is conducted to assess the benefits of a new drug to reduce the recurrence of colonic polyps. A previously healthy 57-year-old woman comes to the physician 1 week after noticing a lump under her right arm. She is concerned that it is breast cancer because both her mother and maternal aunt died of breast cancer. She notes that her skin has never tanned but always burned and freckled when exposed to the sun. The patient says that the lesion has been present for 1 year, but she has never had it examined. Two days after receiving 3 units of packed red blood cells for postpartum hemorrhage, a 24-year-old woman has fatigue and slight jaundice. Cytomegalovirus antibody titer Direct and indirect antiglobulin (Coombs) tests Monospot test Serology for hepatitis B markers Ultrasonography of the gallbladder A 30-year-old man has had nausea, vomiting, and severe colicky right flank pain radiating into the thigh for 4 hours. A 66-year-old woman comes to the emergency department 1 hour after the sudden onset of retrosternal chest discomfort accompanied by nausea and diaphoresis.
Systematic Review of Robotic Surgery in Gynecology: Robotic Techniques Compared with Laparoscopy and Laparotomy allergy medicine 2014 purchase 4mg aristocort, J Minim Invasive Gynecol allergy shots testimonials order genuine aristocort. Use of Guideline Based Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Women Undergoing Gynecologic Surgery, Obstet Gynecol 2013; 122:1145-1153. Can We Rely on Blind Endometrial Biopsy for Detection of Focal Intrauterine Pathology? Substantial functional decline and recurrent or progressive medical illnesses may indicate that a patient who is not eating is unlikely to obtain any significant or long-term benefit from artificial nutrition. Feeding tubes are often placed after hospitalization, frequently with concerns for aspirations, and for those who are not eating. Assistance with oral feeding is an evidence-based approach to provide nutrition for patients with advanced dementia and feeding problems. In this situation, it is reasonable to obtain a urine culture if there are objective signs of systemic infection such as fever (increase in temperature of equal to or greater than 2°F [1. The therapeutic goal of the use of antipsychotic medications is to treat patients who present an imminent threat of harm to self or others, or are in extreme distress not to treat nonspecific agitation or other forms of lesser distress. In fact, studies show that elderly patients with the lowest cholesterol have the highest mortality after adjusting other risk factors. In addition, a less favorable risk-benefit ratio may be seen for patients older than 85, where benefits may be more diminished and risks from statin drugs more increased (cognitive impairment, falls, neuropathy and muscle damage). Appropriate indications for indwelling urinary catheter placement include acute retention or outlet obstruction, to assist in healing of deep sacral or perineal wounds in patients with urinary incontinence, and to provide comfort at the end of life if needed. Benefits of cancer screening occur only after a lag time of 10 years (colorectal or breast cancer) or more (prostate cancer). Patients with a life expectancy shorter than this lag time are less likely to benefit from screening. Prostate cancer screening by prostate-specific antigen testing is not recommended for asymptomatic patients because of a lack of life-expectancy benefit. False positive "test-of-cure" specimens may complicate clinical care and result in additional courses of inappropriate anti-C. Therefore, for some frail elders, the balance of benefits and harms of hospital-level care may be unfavorable. To avoid unnecessary hospitalizations, care providers should engage in advance care planning by defining goals of care for the patient and discussing the risks and benefits of various interventions, including hospitalization, in the context of prognosis, preferences, indications, and the balance of risks and benefits. Patients who opt for less-aggressive treatment options are less likely to be subjected to unnecessary, unpleasant and invasive interventions and the risks of hospitalization. Using a reliable, representative method of taking blood pressures with special attention to orthostatic hypotension is important, as orthostatic hypotension has been associated with increased mortality and cardiovascular events. In addition, moderate or high-intensity treatment of hypertension has been associated with an increased risk of serious falls and injury in frail older adults. Suggested elements were considered for appropriateness, relevance to the core of the specialty and opportunities to improve patient care. A literature search was conducted to provide supporting evidence or refute the activities. The list was modified and a second round of selection of the refined list was sent to the workgroup for paring down to the final "top five" list. Comfort feeding only: a proposal to bring clarity to decision-making regarding difficulty with eating for persons with advanced dementia. The standard of caring: why do we still use feeding tubes in patients with advanced dementia? The risk factors and impact on survival of feeding tube placement in nursing home residents with severe cognitive impairment. The prevalence and persistence of sliding scale insulin use among newly admitted elderly nursing home residents with diabetes mellitus. Management of diabetes mellitus in hospitalized patients: efficiency and effectiveness of sliding-scale insulin therapy. Glycemic control and sliding scale insulin use in medical inpatients with diabetes mellitus.