"Buy atacand 4mg low cost, acute hiv infection stories".
By: O. Raid, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Program Director, Syracuse University
This approach was stimulated by the correlation between the density of the neovasculature in histopathologic specimens and the aggressiveness of the natural history of the disease in a given patient hiv infection natural history order 4mg atacand mastercard. Also stimulating interest in this area was the demonstration in animal models that a number of naturally occurring modulators of angiogenesis also displayed activity in modulating the rate of tumor growth in animal models stages of hiv infection timeline purchase 4 mg atacand mastercard. This has led to the isolation of a large number of agents (synthetic chemicals as well as naturally occurring biologically active proteins) that are known to affect angiogenesis in the treatment of solid tumors and hematopoietic neoplasms. There is immense interest in the current clinical trials of these natural products and naturally occurring proteins to determine whether they are selective for tumor neovasculature or whether they affect the formation of vasculature in normal tissues as well. Computational and combinatorial chemistry is being used to test whether it is possible to develop synthetic inhibitors of angiogenesis that are specific for tumor cell neovasculature. The first step was to test whether computational analysis of the normal angiogenesis receptor could be used to design and synthesize low-molecular-weight chemical inhibitors of the angiogenesis receptor; this has been accomplished (C. Two approaches are being used now to develop chemical therapy that is antiangiogenic. The first is to engineer low-molecular-weight inhibitors of the angiogenesis receptor. This reaction has been shown to depend on the binding of natural killer cells to the Fc fragment of the immunoconjugate molecules. As in many of the other targets we have discussed, the continued expression of these proteins is essential to the maintenance of the neoplastic phenotype. Moreover, since they are viral proteins, those proteins are unique targets that are not essential to the survival or proliferation of normal cells. Thus, drugs developed against these proteins may be highly selective for the tumor tissue and not toxic to the uninfected normal tissue. Additionally, use of the antisense oligonucleotides to these unique targets produces sensitization of these cells to chemotherapy. In the United States, such dysplastic states of the cervical mucosa can be identified by repetitive Papanicolaou smear, and appropriate surgical action can be taken if the dysplasia is severe or persists. Thus, the development of chemicals that will inhibit the formation of viral protein complexes necessary for the assembly of the replication initiation complex could be useful for the development of preventive therapy for cervical cancer. Computational analysis of these surfaces led to predictions about the structure of potential inhibitory compounds, which in turn led to a prospectively randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of drugs in a multiinstitutional setting, sponsored by the National Cancer Institute. It is now possible for a laboratory scientist to recapitulate in a few months what once required millions of years of evolution to produce. The ability to analyze protein structure, to decipher the dynamic array of conformal states of oncoproteins (both activating and inactive), and to characterize the genetic changes that may exert a dominant effect on the natural history of solid tumors and hematopoietic neoplasms (Table 62. Genetic Changes in Solid Tumor and Hematopoietic Neoplasms That Are Suitable Targets for Drug Development the availability of computational chemistry and the ability to generate diversity in chemical structure have enabled scientists to reach beyond the limits of available data about structure and activity relationships and to probe deeply in the unknown repository of untapped chemical structures for molecules that may exhibit favorable binding and specificity properties. It is apparent that the explosion of information about genetic changes in tumor cells will provide the necessary clues with which the chemist can direct structural diversification and screening to isolate newer and more effective compounds. It is possible that this paradigm will be reiterated many times in the development of an entirely new generation of cancer treatment drugs based on inhibitors of receptors, transcription factors, adaptor molecules, viral and somatic cell oncoproteins, and apoptosis rescue proteins. The dividends for cancer patients and society may be substantial in terms of reducing the cost of therapy and enhancing its efficacy. Integrins alpha vbeta3 and alpha v beta5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Three-dimensional structures of H-ras p21 mutants: molecular basis for their inability to function as switch molecules. The presence of the Rb c-box peptide in the cytoplasm inhibits p210bcrabl transforming function. Tyrphostin-induced inhibition of p210bcrabl tyrosine kinase activity induces K562 to differentiate. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. K-ras mutation in colorectal cancer: relations to patient age, sex, and tumor location. Targeting tumor vasculature endothelial cells and tumor cells for immunotherapy of human melanoma in a mouse xenograft model.
The patient did well for approximately 5 years until she presented with a lytic lesion of the posterior parietal scalp hiv infection rates decreasing order atacand 4 mg with amex. Imaging studies revealed a large infiltrating mass compressing the dura and infiltration of the calvarium by angiosarcoma highest hiv infection rate by country discount atacand 16 mg. It has a low potential for metastasis but can behave aggressively and requires excision. B: the same patient many years later demonstrating the effect of neglecting basal cell carcinoma. Long-standing infiltrative basal cell carcinoma of the right cheek in a 95-year-old man. The patient was unable to undergo surgery, and the family declined radiation therapy. This cancer is at high risk for extension into the parotid gland and involvement of the facial nerve. This series depicts a range of pigmented lesions, highlighting those that should arouse a high index of suspicion for malignancy. A melanoma that is up to 1 mm in depth has a 96% cure rate with simple local excision. Any lesion that is suspicious for melanoma or an atypical nevus should be promptly biopsied. The clinical photographs represent the spectrum of pigmented lesions with which patients present to their dermatologist. This very common pigmented lesion has a rough, greasy surface and may often be confused with a melanoma by the patient because of the pigmentation. The visit to the doctor provides an opportunity to perform a full body skin examination. The central lesion is slightly irregular with darker pigmentation in the center surrounded by a rim of tan coloration. These features suggest that this mole may be atypical, especially in comparison to the surrounding nevi. The one on the right is approximately 2 mm in diameter and is regular in coloration. The larger lesion is approximately 5 mm in its longest diameter and has irregular pigmentation. A tangential biopsy is sufficient to determine whether further excision is needed due to the degree of atypicality of the nevus. B: this large nevus has irregular pigmentation, a notched border, and a relative lack of symmetry. It is difficult to identify from the photograph, but one must be concerned about the possibility of an atypical nevus at the least and melanoma at the worst. It has slightly irregular pigmentation that has been unchanged during the life of the patient. Close monitoring is indicated, but biopsy at the earliest sign of any change is necessary. Note how the dark pigmentation is different from surrounding pigmented lesions in this fair-skinned individual. Note the central irregular mole that has a notched border and irregular pigmentation. Careful monitoring of patients with multiple moles may be accomplished with serial photography. Biopsy should be performed on any lesion that demonstrates a change when compared to photographs, or in the opinion of the patient or physician. A congenital mole characterized by large size, brown pigmentation, regular border, and normal skin surface markings. Opinion varies about whether congenital nevi smaller than 1 cm need to be removed. A: Large congenital nevus on the anterior shin of a patient with a history of melanoma. Because of this history it is judicious to ensure that the congenital nevus is removed in its entirety. The author prefers the latter in this situation, as it causes minimal discomfort and provides a superior cosmetic result.
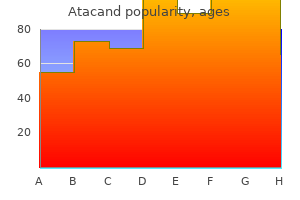
Mantle paraaortic-splenic irradiation after a negative laparotomy occasionally is used as a radiotherapy-alone approach for early-stage disease patients who have not had a staging laparotomy hiv infection rate in india cheap atacand online american express. The paraaortic field encompasses the paraaortic nodes down to the fourth to fifth lumbar vertebral interspace (L4-5) hiv infection rate who order generic atacand line. The dose to the paraaortic lymph nodes should be 3000 cGy when there is no known disease, and radiotherapy alone is used. Beam divergence from the mantle and paraaortic fields creates the potential for an overdose at the spinal cord. Iliac wing blocks to spare bone marrow and a pelvic block to shield the bladder and central pelvic organs should be part of the treatment technique (which includes irradiation of inguinal and femoral nodes). From this model, the authors predicted that response to chemotherapy would depend on tumor burden, drug dose, and kinetics of residual tumor cells. It was further postulated that the simultaneous use of several drugs with different modes of action might yield superior results. The combination of drugs might be tolerated if the toxicities were nonoverlapping. Initial attempts with two-drug combinations revealed the potential of this approach. Further information on chemotherapy is provided in Advanced-Stage Disease later in this chapter. Combined Modality Chemotherapy In addition to the many factors that affect either chemotherapy or radiotherapy when used alone, there are several issues that arise specifically because of potential interaction and summing of effects when they are combined. Failure-free survival was the same in all groups, strongly implying that after optimal chemotherapy, irradiation dose, at least to nonbulky sites, can be reduced without sacrificing efficiency. The risk of two important late complications of irradiation may be reduced by lowering the dose. Stanford University investigators found that a higher dose of irradiation to the mediastinum was associated with increased mortality from cardiac disease. The same theoretic considerations that apply to irradiation are relevant when one considers reduction of the dose of chemotherapy used in combined modality treatment. In theory, either the chemotherapy or the radiotherapy could come first in the sequence of combined modality treatment. In practice, it is almost always desirable for chemotherapy to precede radiotherapy. The reason for this includes early effective treatment of disseminated disease, delay in induction of irreversible loss of bone marrow function, and the opportunity to use smaller, potentially less toxic radiation treatment fields after chemotherapy has induced tumor regression. Implicit in the rationale for this approach is the assumption of a steep dose-response relation for lymphoma patients subjected to chemoradiotherapy. Although care must be exercised in interpreting clinical results, both animal models and clinical studies support the existence of such a relationship. Mucositis and enterocolitis represent the most significant nonhematologic toxicities associated with high-dose melphalan. This information will generally be phrased in terms of probabilities-for instance, the probability of cure for various values of a prognostic factor. It may be used for informing the patient or, in the context of clinical trials, for defining or describing the study population or adjusting the data analysis; however, for the clinician, the most important role of the prognostic factor is to help in selecting an appropriate treatment strategy. Among the remaining patients with early-stage disease who had previously continued to receive radiotherapy alone, an "unfavorable" subgroup often was defined to select patients for combined modality therapy. Each group has thus been associated with a typical standard treatment strategy: Early stages, favorable: radiation alone (extended field) Early stages, unfavorable: moderate amount of chemotherapy (typically four cycles) plus radiation Advanced stages: extensive chemotherapy (typically eight cycles) with or without consolidating (usually local) radiation these "typical" strategies are not uniformly applied, and the investigation of alternatives. In the scheme just listed, two divisions between the three prognostic groups must be noted, each division possibly being defined by a different set of factors. Furthermore, the attempt has been made to identify advanced-stage patients with a particularly high risk of failure for intensified therapy. Prognostic factors are rarely the subject of specific clinical studies but are discovered and evaluated using data from large cohorts of uniformly treated, well-documented, and reliably followed-up patients, usually from large clinical trials. In the following few sections, recognized prognostic factors are described for early stages treated with radiotherapy alone, for early stages treated with chemotherapy, and for advanced stages (treated with chemotherapy), respectively. Such factors are required to show independent prognostic value in multivariate analyses of large numbers of patients.
Enhancing Survival of Immune Cells For T cells to be functional against a tumor antiviral mushrooms buy atacand 8mg with mastercard, they must survive in vivo hiv infection rates bangkok order atacand canada, recognize the target, and then execute an adequate antitumor effector mechanism, either by direct cell lysis or release of cytokines that may attract and stimulate other immune cells. Although adoptive immunotherapeutic strategies have been developed for some cancers, tumor-reactive T cells are difficult to isolate and expand from most types of cancer. A variety of monoclonal antibodies have been developed that bind to specific cancers. Although cancer therapy with antibodies has been largely disappointing, partially because of the lack of an adequate effector mechanism to destroy tumor cells on binding. By combining the antigen-recognition domains from antibodies with the intracellular, signaling chains of T cells, chimeric receptors can be generated that activate T cells based on antibody-like recognition (. This approach, which uses the antigen-binding capabilities of antibodies with the potent antitumor activity of T cells, would allow the production of specific T cells against any antigen for which a monoclonal antibody exists. This strategy could widely generalize the use of adoptive immunotherapy for cancer and infectious diseases. This two-gene strategy, however, is impractical for use in clinical trials using primary T cells, because transduction efficiencies are relatively low for even one gene. Therefore, chimeric receptors encoded on a single gene 148,149 were designed by making use of single-chain antibody variable (scFv) regions in which the light- and heavy-chain variable regions are connected by a flexible linker. In addition, intravenously administered murine T cells transduced with this receptor could specifically treat experimental lung metastases from tumors that express the ovarian cancer antigen. Intraperitoneal administration of these T cells could also successfully treat human ovarian cancer cells growing intraperitoneally in nude mice. This approach has been found to enhance T-cell survival and proliferation in vitro. Transduction of T Cells and Donor Lymphocytes with Suicide Genes Adoptively transferred T cells have been safely administered to many patients for more than 10 years. In an attempt to increase the therapeutic index of adoptively transferred cells in these situations, "suicide" genes can be introduced into lymphocytes to specifically delete the transduced cells should they become toxic to patients in vivo. To optimize this treatment strategy, current efforts are directed toward identifying promoter/enhancer regions that direct higher levels of gene expression in primary lymphocytes. Another approach to cancer gene therapy is to introduce genes into tumor cells that have direct antiproliferative or toxic effects on that cell. This approach, however, requires techniques to directly administer genes into tumor cells in vivo with high efficiencies, which is not technically possible at this time. However, as vector development continues, the direct administration of genes into patients may play a more important role. Some preliminary studies have been initiated that use direct in vivo administration of genes into tumor cells. Some genes, termed tumor suppressor genes, regulate cell growth, and their absence by mutation or deletion results in the malignant phenotype. One approach to treat tumors with deleted or mutated tumor suppressor genes is to replace these genes by in vivo gene transfer. Currently, gene transfer techniques do not exist that are capable of efficiently delivering these genes systemically to all tumor cells in the body, and significant technical improvements are required if this approach is to become practical. Because of this limitation in systemic delivery, several groups have attempted local gene delivery of tumor suppressor genes. Partial response of the injected lesion was observed in 2 of 25 evaluable patients (8%). Several studies have been performed in mice demonstrating in vivo efficacy of antisense oligonucleotides against tumors. A complete response was observed in one of nine patients, with resolution of left axillary lymphadenopathy. In addition, antisense studies must be interpreted carefully, because of the possibility of nonspecific effects. Using this method, tumors regressed, and significant toxicity to surrounding normal tissues was not observed. In situ hybridization revealed that vector producer cells survived up to 7 days in vivo but were associated with only a low level of gene transfer to tumors. In addition, the tumor specificity of this approach is a potential problem, because, in contrast to retroviral vectors, no evidence indicates that adenovirus infects dividing tumor cells preferentially over nondividing normal tissue.
Primary lymphoma of the central nervous system: an unresolved therapeutic problem antiviral treatment cfs 16 mg atacand with visa. Improved survival rate in primary intracranial lymphoma treated by high-dose radiation and systemic vincristine-doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide-prednisolone chemotherapy hiv infection with undetectable viral load purchase atacand toronto. Neurotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents and immunoconjugates delivered after blood-brain barrier modification: neuropathological studies. Preirradiation methotrexate chemotherapy of primary central nervous system lymphoma: long-term outcome. Chemotherapy without radiation therapy as initial treatment for primary central nervous system lymphoma in older patients. Intravenous methotrexate as initial treatment for primary central nervous system lymphoma: response to therapy and quality of life of patients. Intraocular reticulum-cell sarcoma: clinico-pathologic study of four cases and review of the literature. Intraocular reticulum cell sarcoma: its dramatic response to systemic chemotherapy and its angiogenic potential. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in homosexual men: clinical, immunologic, and pathologic features. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in acquired immune deficiency syndrome: a clinical and pathological study. Radiotherapy of primary central nervous system lymphoma in patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus. Long survival in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related primary central nervous system lymphoma. Epstein-Barr virus in monitoring the response to therapy of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome related primary central nervous system lymphoma. He described the disease as a cancer that started and remained in the lymph nodes for a long time, perhaps years, before involving the spleen and then spreading to other organs. Greenfield in 1878 was the first to contribute drawings of them from a low microscopical magnification of a lymph node specimen. Clinical and pathologic studies, available in the early twentieth century, helped to confirm their view. The first peak occurs in the third decade of life, and a second rise in incidence occurs after the age of 50 years. However, population-based studies, using cancer registries in Connecticut and California, convincingly made the argument that the reported clusters occurred by chance alone, and a study that repeated the methodology of Vianna and Poln 11 in a different location failed to confirm their findings. First, another virus could be involved in these cases; however, studies to date have failed to identify another virus. This scarcity of the putative tumor cells was one of the major obstacles for understanding the nature of these cells. Cell Lines and Animal Models the establishment of permanently growing cell lines permitted the biologic and genetic characterization of the tumor cell population in numerous human neoplasias. With few exceptions, all subsequently established cell lines were also obtained from body fluids (bone marrow, pleural effusion, peripheral blood) of advanced-stage patients. This contact results in somatic mutations accumulating in the Ig genes and leading to the expression of antibodies with a higher affinity due to amino acid exchanges. However, somatic mutations might also result in a lower affinity of the antibody or even in generation of a stop codon. All other B cells accumulating favorable mutations are rescued from apoptosis by expressing the bcl-2 gene. These B cells clonally expand and can accumulate further mutations to improve the affinity of their antibody. Thus, proliferating cells with a normal karyotype most probably represent reactive lymphoid cells. In karyotype analyses performed by different groups, the percentage of abnormal karyotypes varied considerably, between 22% and 83%. In a few cases, a loss of chromosomes is reported; for example, chromosomal translocations or deletions were found in two-thirds of cases. Increasing numbers of long-term survivors provided the opportunity to restudy anergy and in vitro lymphocyte responsiveness in patients who have been successfully treated.
Buy atacand 4 mg visa. How AIDS Affects the Body.mp4.