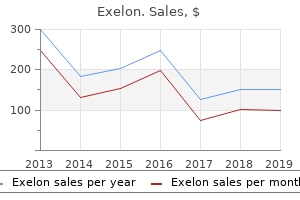
"Cheap 6 mg exelon with visa, medicine 853".
By: J. Brenton, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Extravascular smooth muscle (bronchial treatment 2 stroke effective 3 mg exelon, biliary medications to treat anxiety order exelon toronto, intestinal, vesical, uterine) is also relaxed. These additional mechanisms may account for their predominant smooth muscle relaxant action. Automaticity and conductivity of these cells appear to be dependent on the rate of recovery of the Ca2+ channel. The recovery process which restores the channel to the state from which it can again be activated. Moreover, channel blockade by verapamil is enhanced at higher rates of stimulation, that by nifedipine is independent of frequency, while diltiazem is intermediate. Effect of diltiazem on sinus node automaticity and A-V conduction is similar to that of verapamil. At concentrations which cause vasodilatation they have negligible negative inotropic action which is most prominent in verapamil. Verapamil It dilates arterioles and has some adrenergic blocking activity-decreases t. The pronounced direct cardiodepressant effect is partially offset in vivo by reflex effects of peripheral vasodilatation. Interactions Verapamil should not be given with blockers-additive sinus depression, conduction defects or asystole may occur. It increases plasma digoxin level by decreasing its excretion: toxicity can develop. It should not be used along with other cardiac depressants like quinidine and disopyramide. Diltiazem should not be given to patients with preexisting sinus, A-V nodal or myocardial disease. The direct depressant action on heart requires much higher dose, but a weak negative inotropic action can be unmasked after blockade. Reflex sympathetic stimulation of heart predominates producing tachycardia, increased contractility and c. Tachycardia, propensity to increase cardiac work, flushing, headache, dizziness are subdued. These are related to peaks of drug level in blood: can be minimized by low starting dose or fractionation of dose or use of retard formulation. Ankle edema is not due to fluid retention, but because of greater dilatation of precapillary than postcapillary vessels. By its relaxant effect on bladder nifedipine can increase urine voiding difficulty in elderly males. It has also been reported to hamper diabetes control by decreasing insulin release. Because of less extensive and less variable first pass metabolism, its oral bioavailability is higher and more consistent. It is claimed to attain higher concentration in vascular smooth muscle membrane, and is approved only for use as antihypertensive. As such, it is believed to selectively relax cerebral vasculature and is approved for prevention and treatment of neurological deficit due to cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage or ruptured congenital intracranial aneurysms.
This dose can also be employed for prophylaxis of urinary tract infection following catheterization or instrumentation of the lower urinary tract and in women with recurrent cystitis medications quetiapine fumarate generic exelon 6mg without a prescription. Methenamine (Hexamine) It is hexamethylene-tetramine treatment 3 degree heart block cheap exelon 6 mg free shipping, which is inactive as such; decomposes slowly in acidic urine to release formaldehyde which inhibits all bacteria. This drug exerts no antimicrobial activity in blood and tissues, including kidney parenchyma. Methenamine is administered in enteric coated tablets to protect it from decomposing in gastric juice. Mandelic acid, given as methenamine mandelate, is excreted in urine lowers urinary pH and promotes decomposition of methenamine. It is not an effective drug for acute urinary tract infections or for catheterization prophylaxis. Its use is restricted to chronic, resistant type of urinary tract infections, not involving kidney substance. Adverse effects Gastritis can occur due to release of formaldehyde in stomach-patient compliance is poor due to this. Chemical cystitis and haematuria may develop with high doses given for long periods. Like many other drugs, they are concentrated in the kidney tubules, and are useful mainly in lower urinary tract infection. They have been called urinary antiseptics because this may be considered as a form of local therapy. Nitrofurantoin It is primarily bacteriostatic, but may be cidal at higher concentrations and in acidic urine. Many gram-negative bacteria were susceptible, but due to development of resistance, activity is now restricted largely to E. Probenecid inhibits its tubular secretion and reduces the concentration attained in urine-may interfere with its urinary antiseptic action. Renal excretion is reduced in azotaemic patients; effective concentrations may not be reached in the urine, while toxicity increases. As such, it is contraindicated in renal failure; also during pregnancy and in neonates. Acute infections are largely self limiting; high urine flow rates with frequent bladder voiding may suffice. Though, treatment may not wait till report comes, urine sample must be collected for bacteriology before commencing therapy. It is advisable to select a drug which does not disrupt normal gut and perineal flora. If recurrences are frequent, chronic suppressive treatment with cotrimoxazole, nitrofurantoin, methenamine, cephalexin or norfloxacin may be given. Given once daily at bed time cotrimoxazole 480 mg is often used for prophylaxis of recurrent cystitis in women, as well as in catheterized patients. Parenteral coamoxiclav is often combined with gentamicin for initial treatment of acute pyelonephritis. Cloxacillin Use is restricted to penicillinase producing staphylococcal infection, which is uncommon in urinary tract. Piperacillin/Carbenicillin Only in serious Pseudomonas infection in patients with indwelling catheters or chronic urinary obstructin (prostatic hypertrophy, calculi), and in hospitalized patients on the basis of in vitro sensitivity. Tetracyclines They are seldom effective now, because most urinary pathogens have become resistant. Though broad spectrum, they are used only on the basis of sensitivity report and in Ch. In case of inadequate response or in complicated cases, measurement of urinary pH and appropriate corrective measure may help.
Calcium transport in myocardial and vascular smooth muscle involves: Voltage dependent channel which is controlled by a gate that opens and closes in response to a voltage gradient denivit intensive treatment generic exelon 4.5mg visa. There are 2 types of calcium channels in heart: the L and T: (i) L-channels make the calcium ions available in the cytoplasm medicine 801 discount 3mg exelon amex, that are required for initiation of contraction. Similarly 1 agonists increase calcium influx in, cardiac muscles and enhance contraction, frequency and conduction velocity of heart. It operates bidirectionally to mediate the movement of calcium ions across the sarcolemma. Sarcoplasmic calcium is also regulated by uptake and release of calcium by sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and by buffering of calcium by various intracellular proteins such as calmodulin and troponin C. Further, they can prevent the spasm even in diseased, atherosclerotic coronary arteries. Further, reduction in the afterload contributes to their efficacy in angina of effort. Verapamil and diltiazem have negative inotropic actions and hence should not be combined generally with beta-blockers in the treatment of angina of effort; however, nifedipine can be used together with beta blockers (but see later). This effect plus the improvement of cardiac ischemia accounts for the potent (though selective) antiarrhythmic action. Given orally it is absorbed completely but is substantially metabolised by first pass, hepatic metabolism. It is used in the treatment of angina in the dose of 40-80 mg 3-4 times a day Its use in paroxysmal supra. It has less negative inotropic effect than verapamil and less vasodilating effect than nifedipine and verapamil. It is used either orally or (for a rapid effect) sublingually However, for long term use a sustained release formulation in. Adverse reactions: these include headache, tachycardia, dizziness, fatigue, orthostatic hypotension, leg cramps, skin rashes and gingival hyperplasia. Nifedipine induced arteriolar dilatation in the non-ischaemic zone (there is no further dilatation of arterioles of the ischaemic zone) shunts oxygenated blood away from ischaemic zone to highly perfused non-ischemic zones of the heart. The slower-onset, longeracting calcium blockers such as amlodipine are less likely to cause this phenomenon. Therapeutic uses: Its main use is in the treatment of: (i) Variant angina refractory to nitrate therapy. Nicardipine and isradipine are other dihydropyridine compounds with pharmacological properties and uses similar to those of nifedipine. Nimodipine is related to nifedipine but is claimed to have a preferential vasodilating action on the cerebral arteries in animal studies. Its use is confined to the prevention of vascular spasm and subsequent ischaemic neurological damage following subarachnoid hemorrhage; its usefulness for this purpose is, however, uncertain. Though it preferentially acts on the venous side and reduces the preload, it also acts on the arteriolar side and reduces the afterload. Adverse effects are mostly due to vasodilator action and include headache, dizziness and dose dependent hypotension. Nicorandil is perhaps useful but expensive background therapy for patients with angina pectoris. It is particularly useful as an alternative to nitrates when tolerance is a problem. Dipyridamole: this drug is a coronary dilator; but unlike nitrates which dilate conductance vessels it is claimed to dilate coronary resistance vessels. Calcium abnormalities following cardiac ischemia are associated with disregulation of ion homeostasis, leading to increased intracellular sodium and calcium. Ranolazine is claimed to act by selective inhibition of late sodium influx and thus, prevents calcium overload via the Na+-Ca++ exchanger. It is contraindicated in hepatic impairment and in patients with preexisting Q-T prolongation.
The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms chi infra treatment discount exelon 4.5 mg with mastercard. Gross examination reveals a soft medications may be administered in which of the following ways purchase exelon in india, yellow to gray-white, well-delineated, non-encapsulated, and focally hemorrhagic tumor, encased in red-brown skeletal muscle. Pleomorphic liposarcoma is a high-grade, biologically-aggressive sarcoma with 30% - 50% risk for metastatic potential and 40% - 50% associated mortality. While these tumors can occur in the superficial dermis, these more commonly involve deep, intramuscular locations. The behavior for this pleomorphic adipocytic-phenotype tumor, however, is not as poor as for other pleomorphic sarcomas, including myoid pleomorphic sarcomas (pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma and pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma) and angiosarcoma. Pleomorphic liposarcoma represents the rarest subtype of liposarcoma, accounting for less than 5% of all liposarcomas and 20% of pleomorphic sarcomas overall. By morphology, well-differentiated liposarcoma has adipocytic areas with widened fibrous septa and lipocytic atypia rather than bizarre lipoblasts; dedifferentiation is determined by presence of alipogenic spindled areas representing greater than a 10x power microscopic field (and usually much greater and observed as solid areas on radiologic imaging), with these tumors often 10 Criteria for Diagnosis and Comments located in the retroperitoneum or deep sites. The epithelioid variant of pleomorphic liposarcoma is characterized by sheets of mostly univacuolated to multivacuolated lipoblasts, without intervening spindled and pleomorphic areas. This epithelioid variant of pleomorphic liposarcoma can be keratin positive, making distinction from adrenal and renal clear cell carcinomas difficult; however, these 2 carcinomas ironically often lack keratin. The majority of pleomorphic liposarcomas arise in elderly patients (> 50 years) with an equal sex distribution. Most common anatomic locations for pleomorphic liposarcoma include the extremities (lower > upper limbs), with the trunk and the retroperitoneum being less frequent sites. Rarely the mediastinum, paratesticular region, scalp/neck, abdominal/pelvic cavities, and even orbit may be affected. The differential diagnosis for pleomorphic liposarcoma includes dedifferentiated liposarcoma, pseudolipoblastic melanoma, and pleomorphic carcinomas with vacuolated cytoplasm, including adrenocortical and renal cell carcinoma. Pseudolipoblastic melanoma is a rare variant of melanoma characterized by the presence of intracytoplasmic vacuoles with nuclear scalloping, imparting a pseudolipoblastic appearance. Which of the following criteria can be used to diagnose "pleomorphic liposarcoma" and separate it from "dedifferentiated liposarcoma" Which of the following molecular findings can be used to diagnose pleomorphic liposarcoma Which of the following immunostains would all be positive in epithelioid variant of pleomorphic liposarcoma A clinicopathologic study of 18 cases with emphasis on specific sites, morphologic subtypes and clinical outcome. Liposarcoma with meningothelial-like whorls: a study of 17 cases of a distinctive histologic pattern associated with dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Epithelioid variant of pleomorphic liposarcoma: a study of 12 cases of a distinctive variant of high-grade liposarcoma. She informs the admitting physician that she is being followed by a local gynecologist since the first trimester of the pregnancy and is regularly monitored via ultrasonography due to a placental lesion. According to the information on her chart, no significant complications were noted during her prenatal care except for the presence of a 7. A couple of hours later she vaginally delivers a healthy baby girl without any significant obstetrical complications. The gynecologist examines the placenta and identifies the lesion at the disc margin. The fresh placenta is determined to be appropriate for the estimated gestational age based on its weight and the fetal-toplacental weight ratio. The umbilical cord and fetal membranes fail to demonstrate any gross abnormalities. A marginal ovoid, well circumscribed, and indurated full thickness lesion (resulting in a slight fetal surface bulge) is noted. Master List 5545 2807 2520 2850 2851 Chorangiocarcinoma Chorangioma Chorangiosis Diffuse multifocal chorangiomatosis Localized chorangiomatosis Criteria for Diagnosis and Comments Microscopic evaluation of the lesion reveals a proliferation of capillaries lined by mostly plump endothelial cells associated with scattered larger caliber blood vessels. Other findings include areas of necrosis, hyalinization, calcification, and hemorrhage. Patchy acute inflammation is present, mostly in association with the necrotic areas. In a few foci, the surface of the lesion is covered by a mild non-atypical syncytiotrophoblastic proliferation.
The only complete trisomies that are compatible with extrauterine life are those of certain small autosomes: trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) medicine x 2016 buy exelon online pills, trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome) symptoms ulcerative colitis purchase exelon online from canada, and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome). Therefore, with these exceptions, the only autosomal aberrations that one encounters clinically are 1) mosaic states for either trisomies or monosomies, in which only some cells in the body are affected; or 2) more commonly, partial monosomies or trisomies, in which only a portion of an autosome is misrepresented. There are hundreds-perhaps thousands-of these partial monosomies and trisomies, of which only a few are well-recognized clinical entities. As a general rule, there are four cardinal clinical features of an autosomal aberration disorder: 1) intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation; 2) a pattern of dysmorphic features, usually involving the face, limbs, and genitalia; 3) malformations, usually involving multiple organ systems; and 4) severe dysfunction of the nervous system. In most described autosomal aberration syndromes, neuroradiologic features have not been studied systematically. Autosomal Trisomies Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Described by Down in 1866, trisomy 21 is the most common chromosomal disorder and a lead- ing cause of mental retardation. Right lateral view demonstrates the typical small superior temporal gyrus (between white arrowheads) and rounded configurations of the brain. D, Coronal section of C displays small superior temporal gyri (white arrowheads) bilaterally. Right lateral view demonstrates an open sylvian fissure (arrow) resulting from hypoplasia of the inferior frontal gyrus and the superior temporal gyrus. F, Sagittal Tl-weighted image of the cervical spine in a patient with Down syndrome demonstrating cord compression at Cl, due to atlanto-axial dislocation (arrows) with abnormal forward angulation of the cervico-medullary junction. Note the short rounded contour of the skull and brain with narrow frontal lobes, a feature of Down syndrome. The same mechanism is thought to be a general phenomenon responsible for many aneuploidies. Several different abnormalities of chromosome 21 are associated with Down syndrome: 1. Down syndrome, translocation type: About 4 % of Down syndrome results from this mechanism. However, the extra chromosomal material is either a de novo event or derives from the inheritance of a parental chromosome having a translocation of the long arm of chromosome 21 to another acrocentric chromosome, usually 22 or 14. Since the fertilized ovum already possesses two normal autosomes 21, the translocated material provides triplication of some of the genes, as occurs in trisomy 21. B, Neonatal photograph illustrates the dolichocephaly, low-set ears and micrognathia common in trisomy 17- 18. The hands characteristica lly exhibit flexion and overriding of fingers bilaterally. C, Coronal section of the brain displays poor delineation of the right superior, m iddle, and inferior temporal gy ri and of the left inferior temporal gyrus. The symptoms of translocation Down syndrome are identical with those of the trisomy Down syndrome. In translocation Down syndrome, however, there is no effect of maternal age on the risk of recurrence; 3. Down sy ndrome, mosaic ty pe: About 2 % -3 % of Down sy ndrome cases are mosaics having a mixture of cells with either 46 or 47 chromosomes. The facial features of trisomy 21 include brachycephaly; hypoplasia of the maxillae and nasal bones with flattening of the nasal bridge, orbital ridges, and maxillae; ocular hypotelorism; oblique palpebral fissures; epicanthal folds; spotting of the iris (Brushfield spots); cataracts; strabismus (one-third of patients); protruding fissured tongue with hypertrophied papillae; and small ears. These patients tend to develop Alzheimer disease at an early age, with senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles ultrastructurally identical with those seen in typical cases of Alzheimer disease. When examined at autopsy, the brain is reduced in weight (rarely exceeding 1,000 g) and is abnormally round. A narrow superior temporal gyrus is a characteristic developmental abnormality observed in half the patients with Down syndrome. Specimen photograph reveals semilobar holoprosencephaly with partially collapsed dorsal cyst and focal lissencephaly. C and D, Semilobar holoprosencephaly 1-day-old girl born prematurely at 29-30 weeks gestation.
Discount 6 mg exelon overnight delivery. Can Shakeology help MS symptoms? Review by Daryl H Bryant.